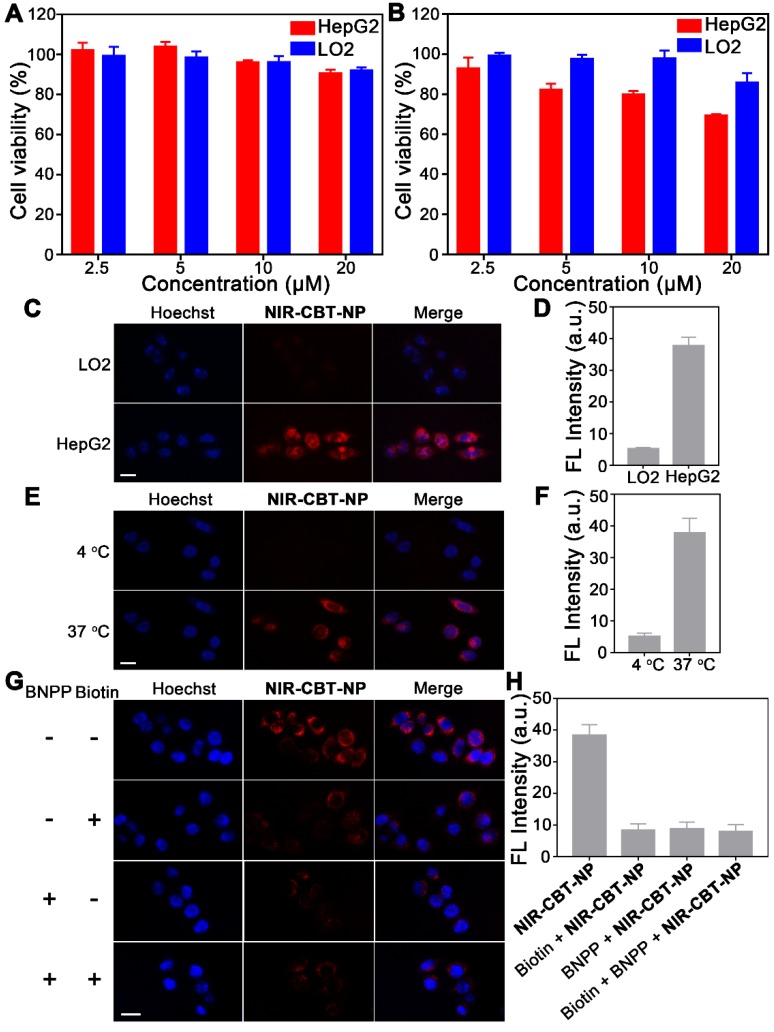
Figure 4.
MTT assays of NIR-CBT-NP on LO2 cells and HepG2 cells for 6 h (A) and 72 h (B). The experiments were performed in triplicate. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations. (C) Fluorescence and overlay images of LO2 cells (top row) and HepG2 cells (bottom row) after incubation with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP at 37 °C for 6 h. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) The mean Cy5.5 fluorescence intensity from LO2 cells or HepG2 cells in C. (E) Fluorescence and overlay images of HepG2 cells after incubation with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP at 4 °C (top row) or 37 °C (bottom row) for 6 h. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) The mean Cy5.5 fluorescence intensity from HepG2 cells in E. (G) Fluorescence and merged images of biotin receptor-positive and CES-overexpressing HepG2 cells after incubation with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP at 37 °C for 6 h (top row), or pretreated with 1 mM biotin at 37 °C for 1 h then incubated with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP for 6 h (top middle row), or pretreated with 100 μM BNPP for 1 h then incubated with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP for 6 h at 37 °C (bottom middle row), or pretreated with 1 mM biotin and 100 μM BNPP for 1 h then incubated with 20 μM NIR-CBT-NP for 6 h at 37 °C (bottom row). Hoechst 33342 (blue), nuclear counterstaining. Red fluorescence, Cy5.5 in NIR-CBT-NP. Scale bar, 20 μm. (H) The mean Cy5.5 fluorescence intensity from HepG2 cells in G.