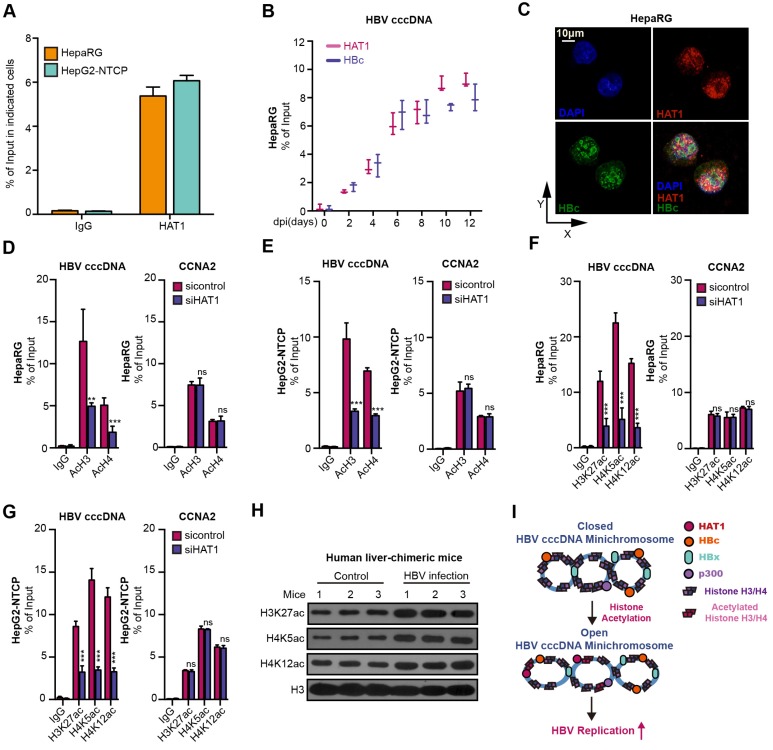
Figure 3.
HAT1 promotes histone acetylation on HBV cccDNA minichromosome. (A) The deposition of HAT1 on cccDNA was measured by ChIP-qPCR in the HBV-infected dHepaRG and HepG2-NTCP cells. (B) The deposition of HAT1 and HBc on cccDNA was analyzed by ChIP-qPCR at indicated time in the HBV-infected dHepaRG cells. (C) The colocalization of HAT1 and HBc was assessed 8 dpi by confocal microscopy in the dHepaRG cells. (D-G) The acetylation of histone, including AcH3, AcH4, H3K27ac, H4K5ac and H4K12ac, associated to cccDNA minichromosome or the promoter of CCNA2 was verified 8 dpi by ChIP-qPCR in the dHepaRG and HepG2-NTCP cells. (H) The acetylation of histone H3K27, H4K5 and H4K12 were examined by Western blot analysis in the liver of human liver-chimeric mice (n=3) and HBV-infected human liver-chimeric mice (n=3). (I) A model for the function of HAT1 in promoting histone acetylation of cccDNA minichromosome was shown. Mean ± SD of at least three experiments are shown, in which each experiment was designed by three replicates. Statistical significant differences are indicated: **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ns, no significance.