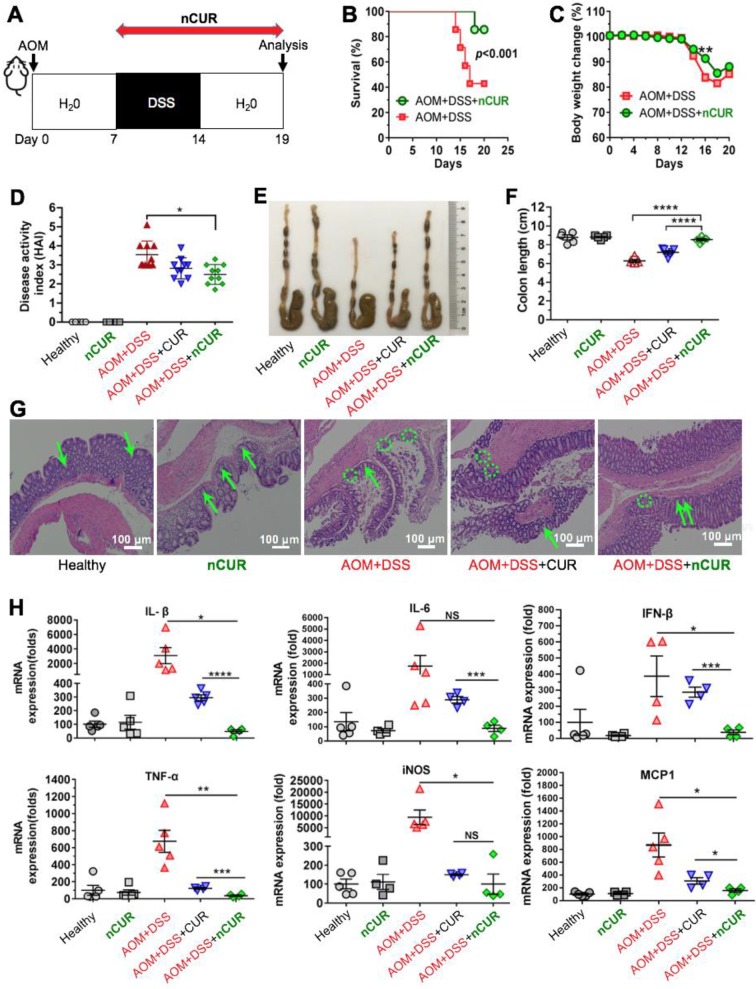
Figure 4.
Treatment with nCUR alleviates colitis at the early stage of CAC. (A) A schematic overview of the DSS-induced colitis model in C57BL/6 mice. The mice were injected with AOM followed by supplementation with 3% DSS in water for seven days. For anti-inflammatory treatment, nCUR was given daily in water by drinking ad libitum. The mice were euthanized on day 19 after AOM injection. (B) Treatment with nCUR improved survival in mice with DSS-induced fatal colitis (n = 7 mice in each group). Kaplan-Meier survival curves were compared by the log-rank test. (C) Weight loss was monitored throughout the therapeutic studies. (D) The disease activity index (DAI) was evaluated on day 19 after AOM injection. DAI is the summation of the stool consistency index, fecal bleeding index, and weight loss index. (E) Colons were photographed, and (F) colon lengths were measured at the end of the therapeutic studies. (G) Representative H&E staining of the mouse colon. The green arrows and dotted circles indicate crypts and leukocyte infiltration, respectively. (H) Relative expression of inflammatory cytokines in the murine colon on day 19 after the induction of colitis in mice. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. N.S. indicates no significant difference; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.