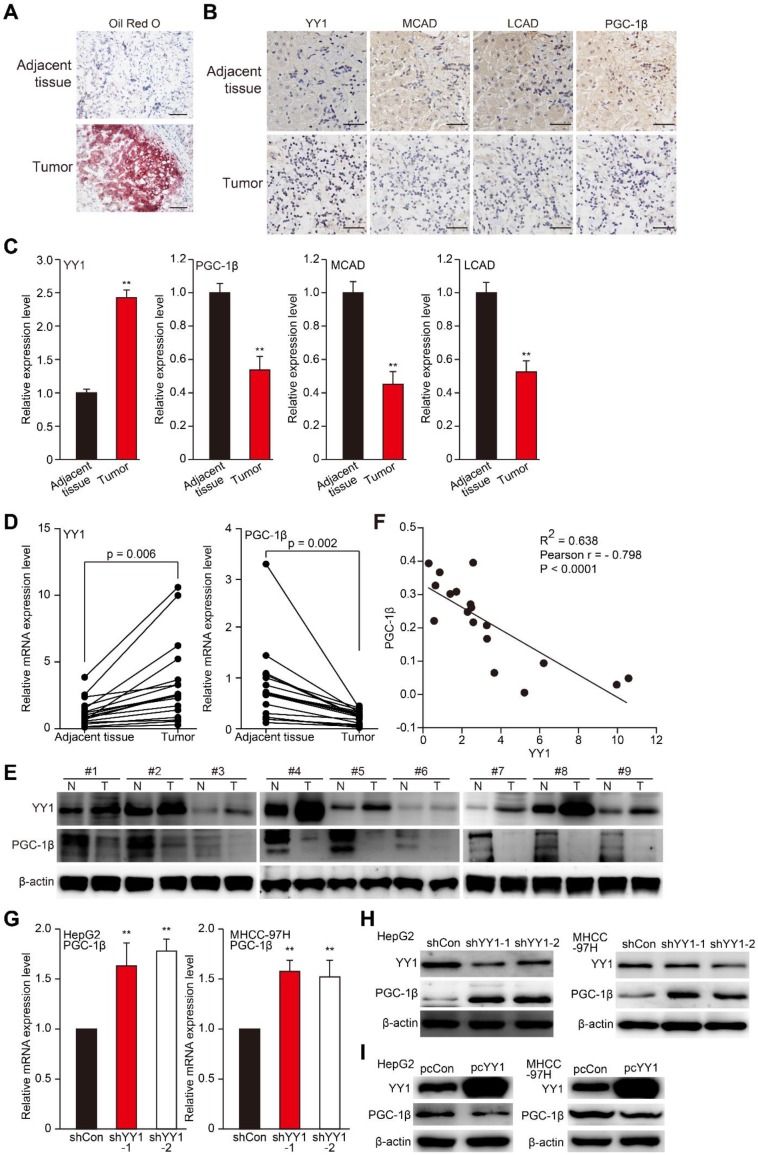
Figure 3.
YY1 negatively regulates PGC-1β at the transcriptional level in HCC cell. A. The accumulation of lipid droplets in the clinical HCC tissue and the normal adjacent tissue, as analyzed using Oil Red O staining. Scale bars: 200 μm. B-C. The expression levels of YY1, MCAD, LCAD and PGC-1β in the clinical HCC tissue and the normal adjacent tissue, as analyzed by immunohistochemical staining using serial sections. Representative images (B) and the quantification results (C, n = 6) are shown. Scale bars: 40 μm. Quantification results are shown as relative to adjacent tissue. D-E. The mRNA (D, n = 18) and protein (E, n = 9) expression levels of YY1 and PGC-1β in clinical human HCC and the corresponding normal adjacent tissues. F. Correlation analysis between the mRNA expression levels of YY1 and PGC-1β in clinical HCC tissue. G-H. PGC-1β mRNA (G) and protein (H) expression levels in YY1-silenced HepG2 and MHCC-97H cells cultured under hypoxic condition, as determined using qRT-PCR (n = 3) and western blotting, respectively. I. PGC-1β protein expression levels in YY1-overexpressed HepG2 (left) and MHCC-97H (right) cells cultured under hypoxia, as determined using western blotting. Cells transfected with shCon or pcCon were used as controls. β-actin was used for qRT-PCR normalization and as western blotting loading control. Quantification data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. pcCon: pcDNA3.1(+); **P < 0.01 (ANOVA).