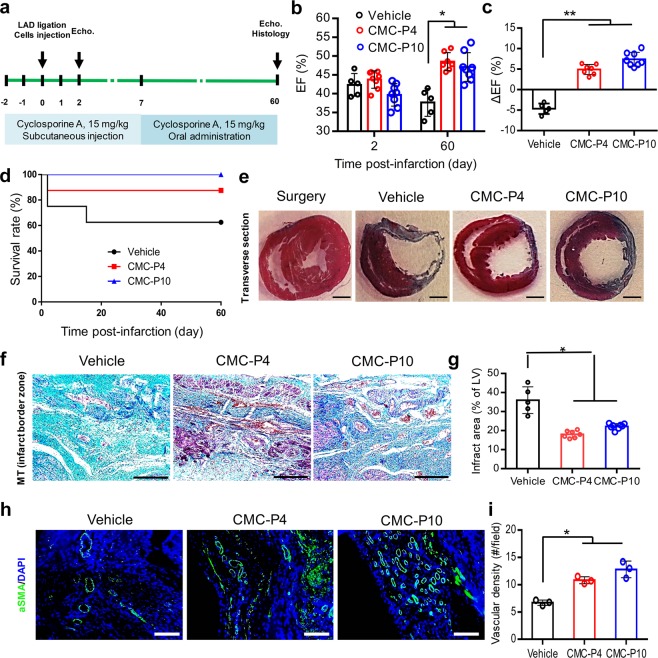
Figure 7.
Cardio-protective effect of adherently expanded CMCs in ABC medium after transplantation into rat infarcted myocardium. (a) Schematic outline of the in vivo experiment. The animals received intramyocardial injections of the cells into the infarct border zone, 20 min after LAD artery ligation. Animals were immunosuppressed by the administration of cyclosporine A. Echo: Echocardiography. (b) The ejection fraction (EF) index of heart performance as evaluated by Echo at 2 and 60 days post-infarction. The data showed a significant increase of EF in the cell injected groups compared to the vehicle group. (c) The ΔEF represents the difference between the EF values measured at days 2 and 60 post-infarction for the in vivo groups. (d) Kaplan-Meier survival rate analysis of different in vivo groups. The cell transplanted groups had a higher survival rate compared to the vehicle group. (e) Masson’s trichrome (MT) stained transverse sections of rats’ hearts 60 days after infarction. Scale bar: 2 mm. (f) Cardiac fibrotic tissue stained with MT at the infarct border zones. Scale bars: 200 µm. (g) The measured infarct fibrotic area (%) stained by MT indicated significantly decreased scar tissues in the cell transplanted groups compared to the vehicle group. (h) Representative immunostaining against vascular structures with anti-αSMA. (i) The quantification indicated that the significant higher vascular densities in cell transplanted groups compared to vehicle group. Scale bars: 200 µm. LV: Left ventricle. All data: mean ± SD and statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01.