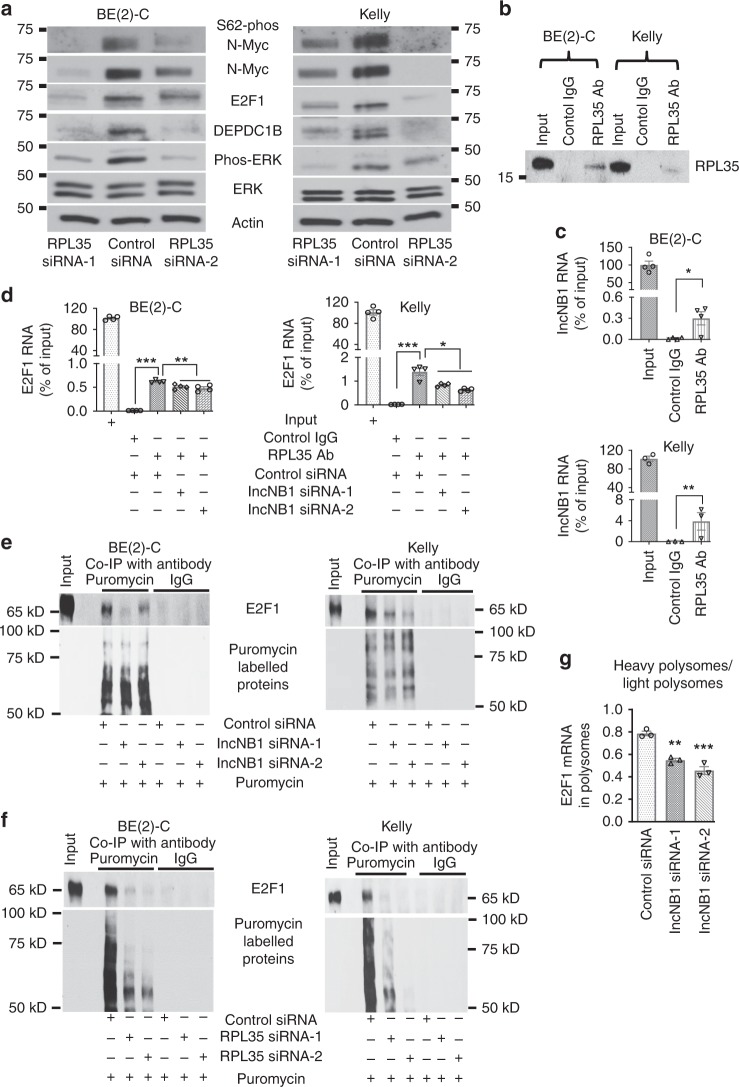
Fig. 5.
LncNB1 increases E2F1 protein translation by binding to the ribosomal protein RPL35. a BE(2)-C and Kelly cells were transfected with control siRNA, RPL35 siRNA-1, or RPL35 siRNA-2 for 48 h, followed by immunoblot analysis of DEPDC1B, ERK, phosphorylated ERK (phos-ERK), N-Myc, S62-phos-N-Myc, and E2F1 protein expression. b–d RNA immunoprecipitation assays were performed with a control IgG or an anti-RPL35 antibody (Ab) without siRNA transfection (b, c) or after transfection with control siRNA, lncNB1 siRNA-1, or lncNB1 siRNA-2 (d) in BE(2)-C and Kelly cells. Immunoprecipitated protein was immunoblotted with the anti-RPL35 antibody (b), and immunoprecipitated RNA was examined by RT-PCR with primers targeting lncNB1 (c) or E2F1 (d). e, f BE(2)-C and Kelly cells were transfected with control siRNA, lncNB1 siRNA-1 or siRNA-2 (e) or RPL35 siRNA-1 or RPL35 siRNA-2 (f) for 48 h, followed by labeling with puromycin (10 µg/ml) for 15 min. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was performed with a control IgG or anti-puromycin antibody and immunoblot with anti-E2F1 and anti-puromycin antibodies. g BE(2)-C cells were transfected with control siRNA, lncNB1 siRNA-1, or lncNB1 siRNA-2 for 48 h, followed by treatment with 50 µg/ml of cycloheximide and polysome fractionation. RT-PCR analysis of E2F1 mRNA was performed and results were pooled into light (fraction 7, 8, and 9) and heavy (fraction 12, 13, and 14) polysomes and expressed as the ratio of mRNA in heavy polysomes and mRNA in light polysomes. In c, d, g data were shown as the mean ± standard error of three or four independent experiments, and evaluated by two-sided unpaired Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA. *, **, and *** indicate P < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file