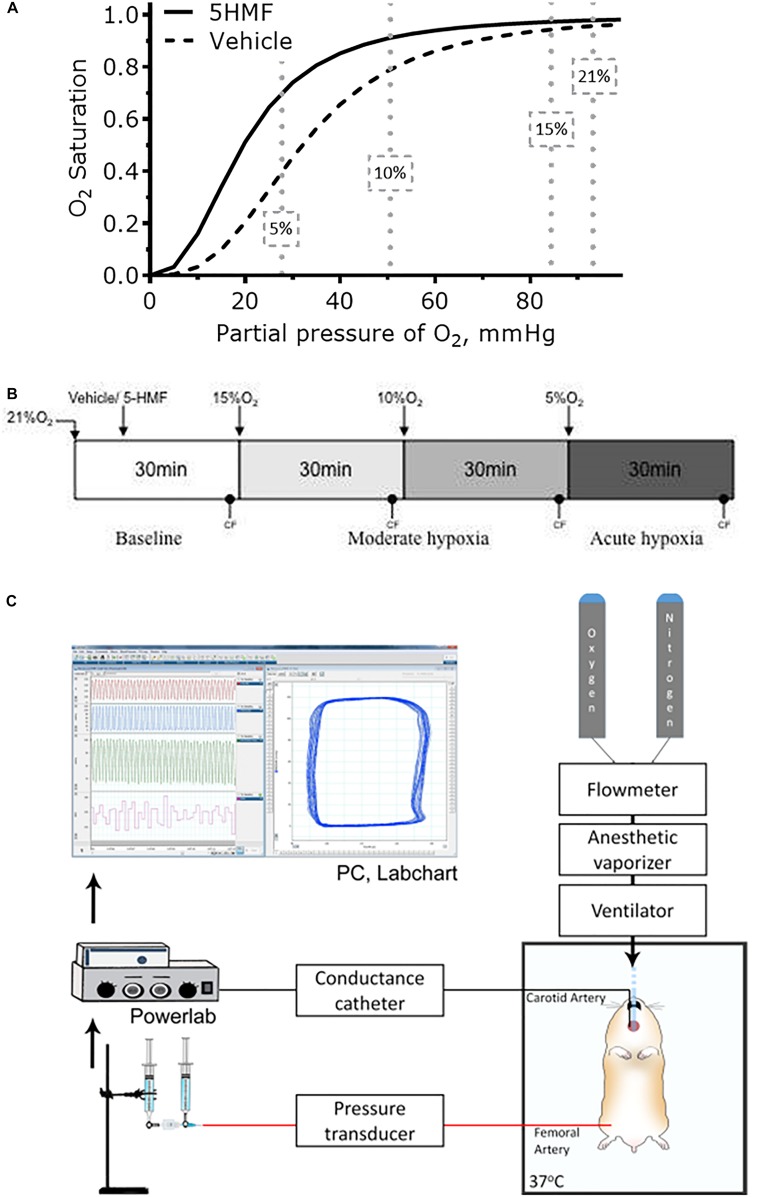
FIGURE 1.
(A) Changes in blood Hb-O2 equilibrium during normoxia and hypoxia. 5-HMF increased blood Hb-O2 equilibrium in a dose dependent matter. At 10 and 5% O2, arterial Hb-O2 saturation should be higher with a left shift in the Hb-O2 dissociation curve (Kurti and Czako, 2005). (B) Hypoxia scheme followed in the experiments. After 5-HMF or the vehicle, animals were exposed to hypoxia by decreasing the fraction of inspired O2 (FiO2)stepwise from 15% to 10%, and then to 5% O2. Each hypoxic step was maintained for 30 min. (C) Representation of the experimental setup. Hamster was maintained on a 37°C heated platform. Tracheotomy was performed to achieve consistent mechanical ventilation and volatile anesthesia administration. Compressed gases (100% O2 and 100% N2) were connected to a flowmeter tonometer to adjust achieve desired FiO2. Flowmeter tonometer provided gases to anesthesia vaporizer and ventilator. Conductance catheter (MPVS3000, Millar Instruments) was inserted through the carotid artery and advanced to the LV. Femoral artery was catheterized for blood samples and blood pressure measurements. Jugular vein was catheterized for fluid infusions. CF and MAP measurements were collected using data acquisition hardware (PowerLab 8/30, AD Instruments), attached to a personal computer, and stored for off-line analysis using PVAN software (PVAN 3.6, Millar Instruments). Parallel volume was calibrated at the end of the experiment via IV injection of 10 μL hypertonic saline (10% NaCl) (Pacher et al., 2008).