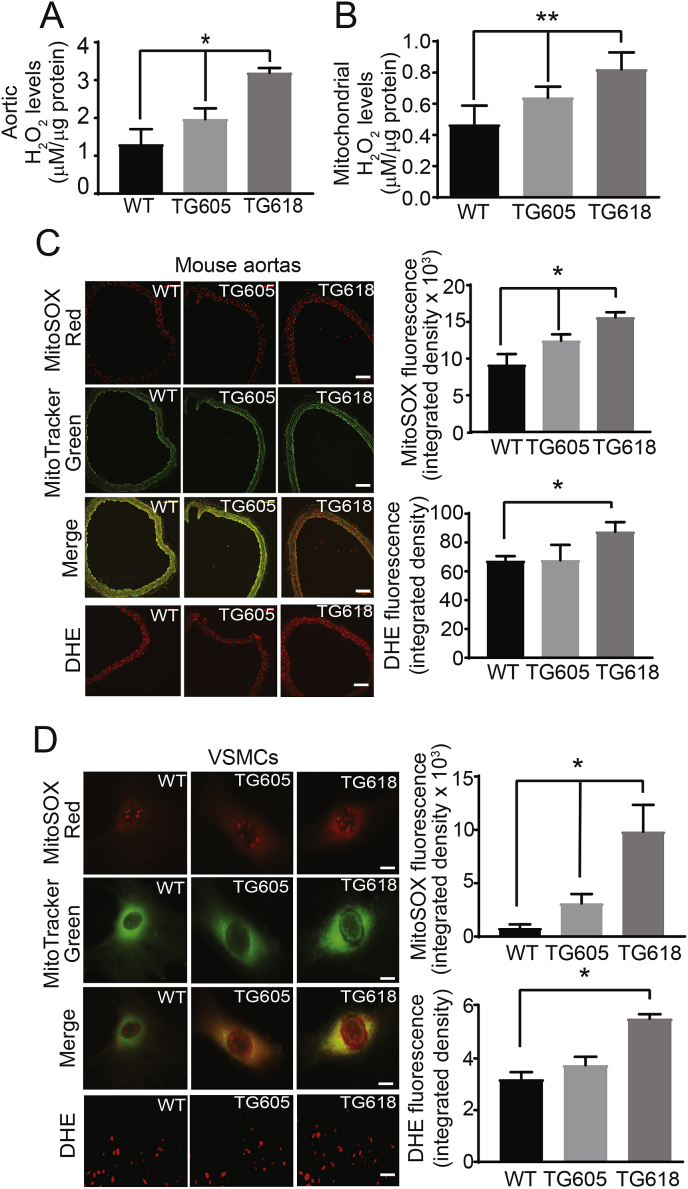
Fig. 6.
Increase in mitochondrial NOX4 protein levels is correlated with enhanced H2O2 and ROS levels in whole aortas and aortic VSMCs. (A) Aortic H2O2 levels were determined using Amplex Red assay and normalized to protein levels (mean ± SEM, N = 5). (B) VSMC mitochondrial H2O2 levels were determined using Amplex Red assay. H2O2 levels are normalized to protein concentration and are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (C) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of aortic sections stained with MitoSOX Red and MitoTracker Green FM. Bright yellow/orange fluorescence indicates increased mitochondrial ROS generation in medial VSMCs. Scale is 100 μm. Data presented as integrated density of MitoSOX Red fluorescence (mean ± SEM, N = 5). Representative DHE fluorescence microscopy images and quantification of DHE fluorescence in medial VSMCs (mean ± SEM, N = 5). Scale is 100 μm. (D) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of VSMCs stained MitoSOX Red and MitoTracker Green FM. Bright yellow fluorescence indicates increased ROS generation. Data presented was integrated density of MitoSOX Red fluorescence (mean ± SEM, N = 30). Scale is 10 μm. Representative DHE fluorescence microscopy images and quantification of DHE fluorescence in VSMCs (mean ± SEM, N = 30). Scale is 10 μm *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)