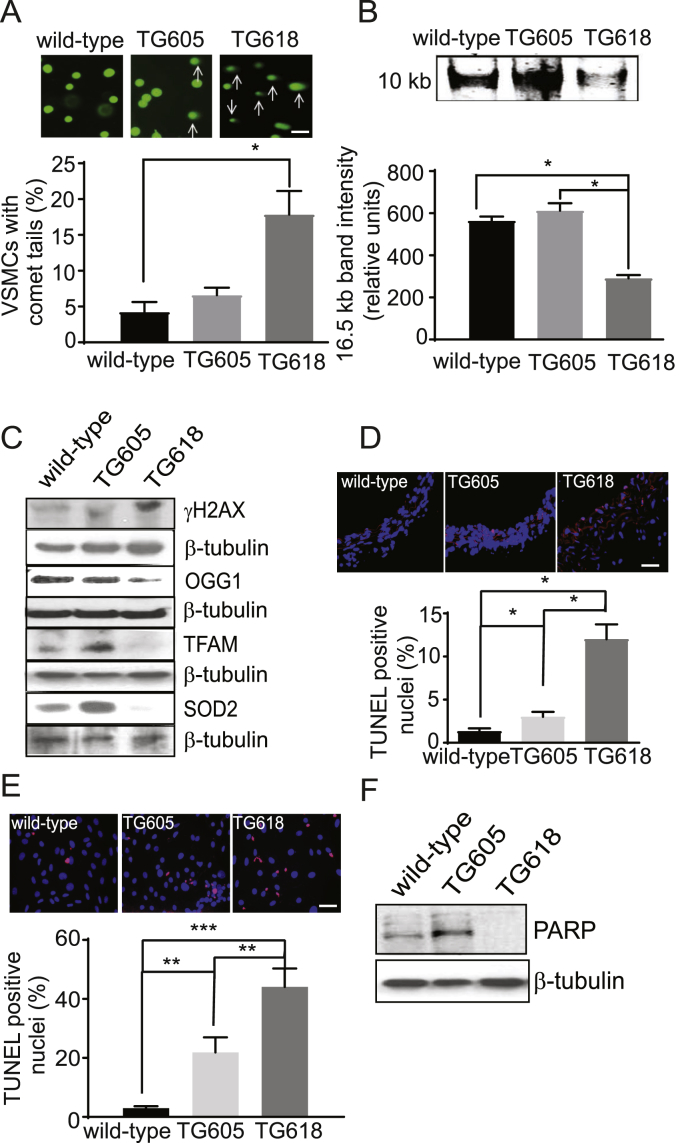
Fig. 7.
Young Nox4TG mice show increased DNA damage and apoptosis in VSMCs. (A) Representative comet assay images and quantification of cells with comet tails in aortic VSMCs isolated from wild-type and Nox4TG mice. Percent of cells with comets from 15 microscopic areas from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM, N = 3). (B) Representative long PCR amplicon showing decreased 10 kb mitochondrial DNA in VSMCs from wild-type, Nox4TG605, and Nox4TG618 mice. The amplified 16.5 kb mitochondrial genome band intensity was normalized to a short PCR amplicon of 0.22 kb GAPDH (mean ± SEM, N = 3). (C) Representative Western blots of VSMC lysates indicate more DNA damage and increased oxidative stress, as shown by increased levels of γH2AX and decreased levels of OGG1, TFAM, and SOD2 in Nox4TG618 versus Nox4TG605 and wild-type mice. (D) Representative fluorescent microscopy images of TUNEL-stained aortic sections showing increased TUNEL+ nuclei in medial VSMCs of Nox4TG618 versus Nox4TG605 and wild-type mice. Quantification of TUNEL+ nuclei (mean ± SEM, N = 3). (E) Representative fluorescent microscopy images of TUNEL-stained VSMCs showing increased TUNEL+ nuclei in Nox4TG618 versus Nox4TG605 and wild-type VSMCs. Quantification of TUNEL+ nuclei (mean ± SEM, N = 3). (F) Western blot analysis of PARP expression levels in aortic VSMCs of wild-type and Nox4TG mice. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.