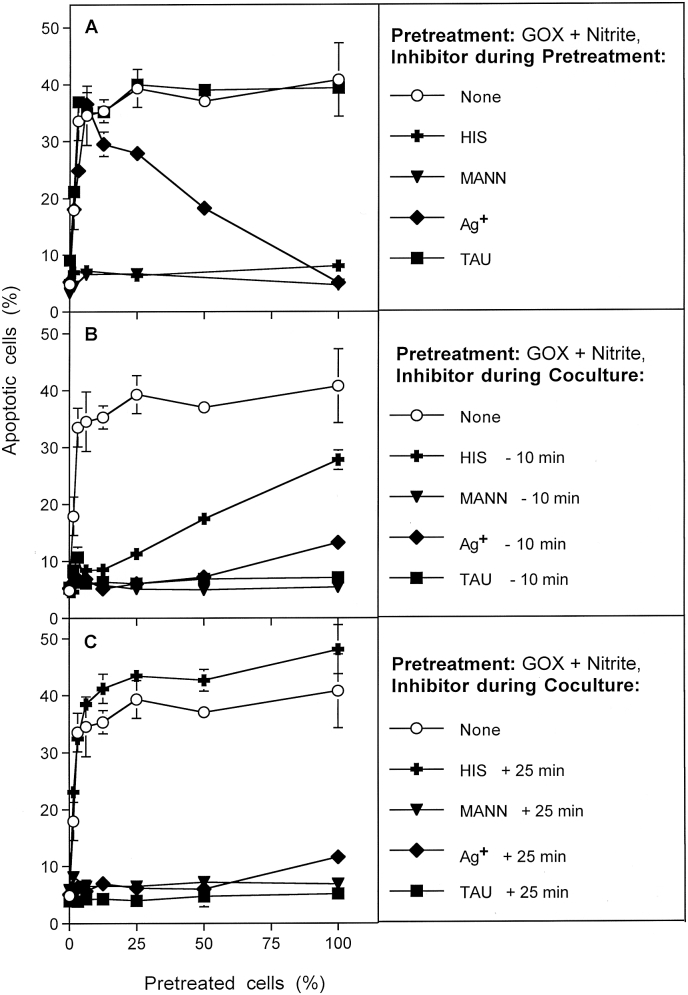
Fig. 5.
Determination of the potential roles of singlet oxygen, hydroxyl radicals, aquaporins and HOCl for bystander signaling. MKN-45 cells were pretreated with 0.05 mU/ml GOX and 1 mM nitrite for 25 min, subjected to three cycles of washing and then resuspended in fresh medium. Pretreated cells were added at increasing percentages to untreated tumor cells. A. During pretreatment with GOX/nitrite, additional assays received 2 mM histidine, 20 mM mannitol, 5 μM Ag+ or 50 mM taurine. B. During coculture of GOX/nitrite-pretreated cells with untreated cells, histidine, mannitol, Ag+ or FeTPPS were also present. The inhibitors had been added to the cells 10 min before mixing the populations. C. The experiment was performed as described under B, with the modification that the inhibitors had been added 25 min after the beginning of coculture. In all assays, the percentages of apoptotic cells were determined at 4 h. These results show that singlet oxygen plays a central role for activating the bystander effect-inducing cells and within the first 25 min of coculture for transmission of bystander signaling. Hydroxyl radicals seem to play a role in early and late steps, in line with multiple roles in this scenario. Aquaporins play no role for activation and transmission bystander signaling, but seem to play a role for allowance of intercellular apoptosis-inducing signaling. HOCl plays no role for activating bystander signaling and its transmission, but are of central importance for apoptosis inducing signaling. Statistical analysis: A: Inhibition by histidine and mannitol is highly significant (p < 0.001), whereas taurine causes no significant inhibition. Ag+ does not cause significant inhibition up to 25% pretreated cells, but causes highly significant inhibition (p < 0.001) at higher percentages of pretreated cells. B: All inhibitors caused highly significant inhibition (p < 0.001). The differences seen for the histidine-mediated inhibition curve compared to the curves obtained with the other inhibitors are highly significant (p < 0.001). C. All inhibitors cause highly significant inhibition (p < 0.001), except for histidine.