Figure 5.
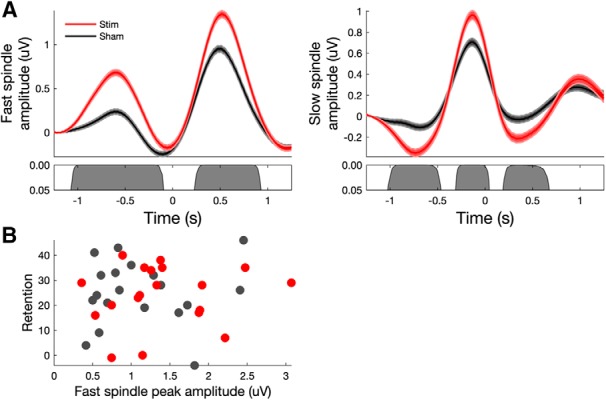
Acoustic stimulation enhances both fast- and slow-spindle amplitude but is not related to verbal memory consolidation. A, Fast-spindle (12–15 Hz) and slow-spindle (9–12 Hz) amplitude at electrode Cz time locked to the negative DOWN state of all detected SO events (t = 0). B, Scatter plot of retention versus peak fast-spindle amplitude across individuals in sham and stimulation conditions (not significant in either condition).
