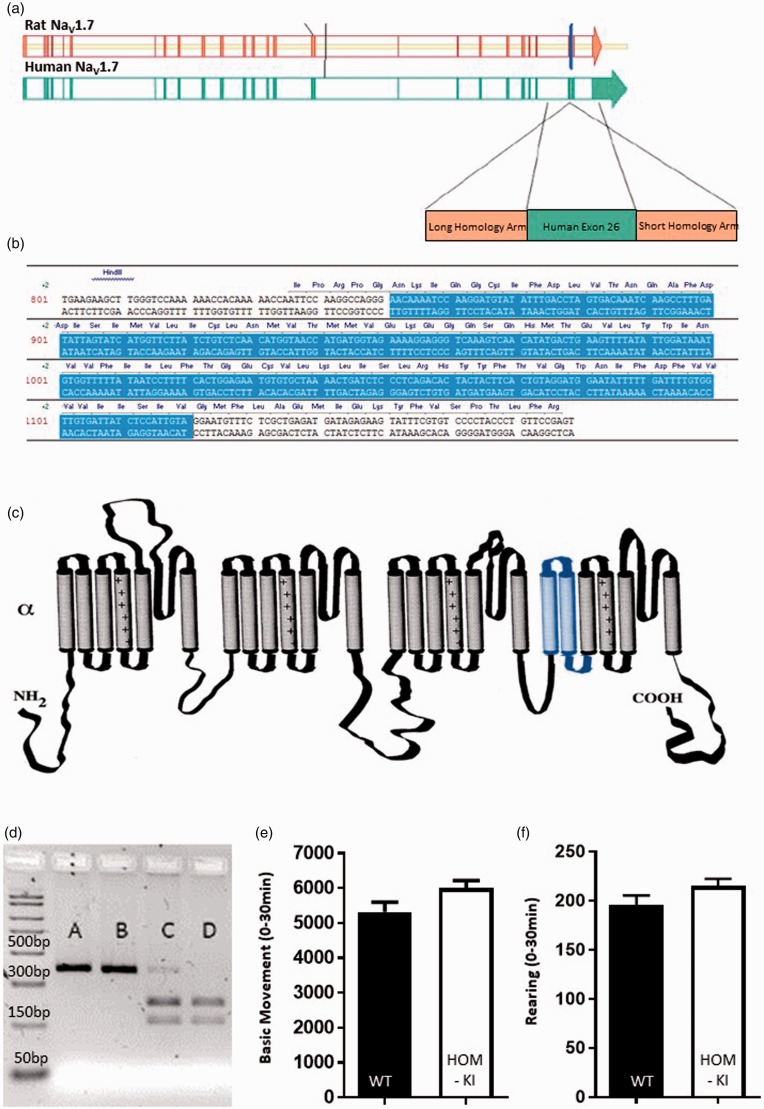
Figure 1.
Strategy to generate humanized chimeric NaV1.7 rat. (a) Rat NaV1.7 exon 25 (blue vertical line) was replaced with the corresponding sequence in human NaV1.7, which is human exon 26. (b) Schematic representation of the Human NaV1.7 exon 26 sequence (blue shading) inserted into rat NaV1.7 sequence (white shading) to generate the resulting chimeric NaV1.7 channel. (c) Predicted topology of rat NaV1.7 protein with insertion of human exon 26 coding sequence (blue shading) comprised of the first two transmembrane domains and S2-S3 intracellular loop of domain IV. (d) Representative restriction digest analysis of PCR products originating from genomic DNA from HOM-KI (A and B), HET (C) and WT (D) rats. (e) Open-field basic movement assessment. HOM-KI (5997 ± 220 counts) and WT (5318 ± 281 counts) rats had similar levels of exploratory movement (t18 = 1.9, p = 0.07, unpaired t-test, n = 10/group). (f) Open-field rearing count assessment. HOM-KI (215 ± 7 counts) and WT (196 ± 10 counts) rats had similar rearing counts (t18 = 1.6, p = 0.13, unpaired t-test, n = 10/group). (Data are mean ± SEM).