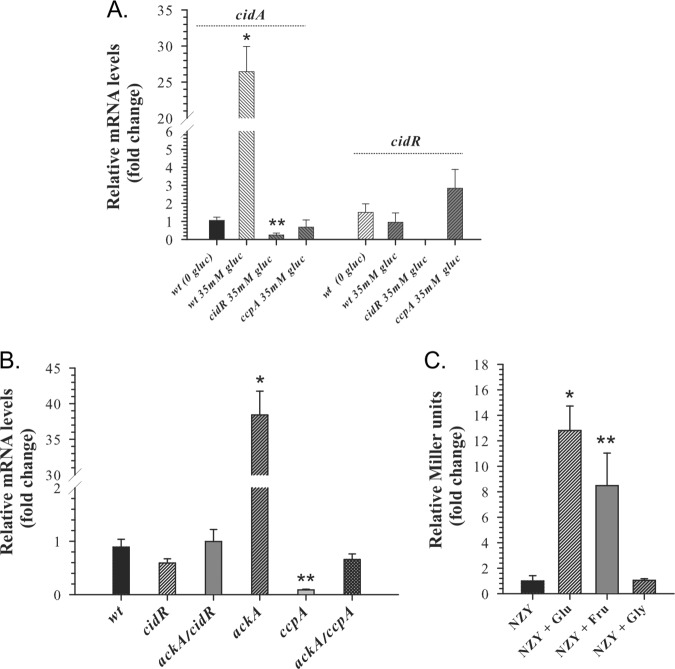
FIG 3.
CcpA is required for induction of cidABC expression. (A) Relative transcript levels of the cidA and cidR genes determined by quantitative RT‐PCR after 6 h of growth. Transcript levels in the wild-type strain, cidR, and ccpA mutants grown in TSB containing 35 mM glucose (inducing conditions) are presented as a fold difference compared to those for the wild-type strain grown in TSB without glucose. Statistical significance between the wild‐type strain grown with or without glucose (*) as well as between the cidR mutant grown under inducing conditions and wild‐type strain grown in the absence of glucose (**) was determined by Student's t test (P ≤ 0.01). (B) Relative cidA transcript levels determined by quantitative RT‐PCR after 3 h of growth in TSB containing 14 mM glucose. Transcript levels in the cidR, ackA, ccpA, ackA cidR, and ackA ccpA mutants are presented as fold differences compared to those in the wild‐type strain. Statistical significance between the wild‐type strain and ackA mutant (*) and between the wild‐type strain and ccpA mutant (**) was determined by Student's t test (P ≤ 0.005). (C) Effect of alternative carbon sources on cidABC expression. Wild‐type strain cultures containing the PcidABC-lacZ reporter plasmid were grown either in plain NZY medium or NZY medium supplemented with 35 mM glucose, 42 mM fructose, or 70 mM glycerol. After 6 h of growth, samples were collected and assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Statistical significance between the wild‐type strain grown in plain NZY and NZY supplemented with glucose (*) or fructose (**) was determined by Student's t test (P ≤ 0.01).