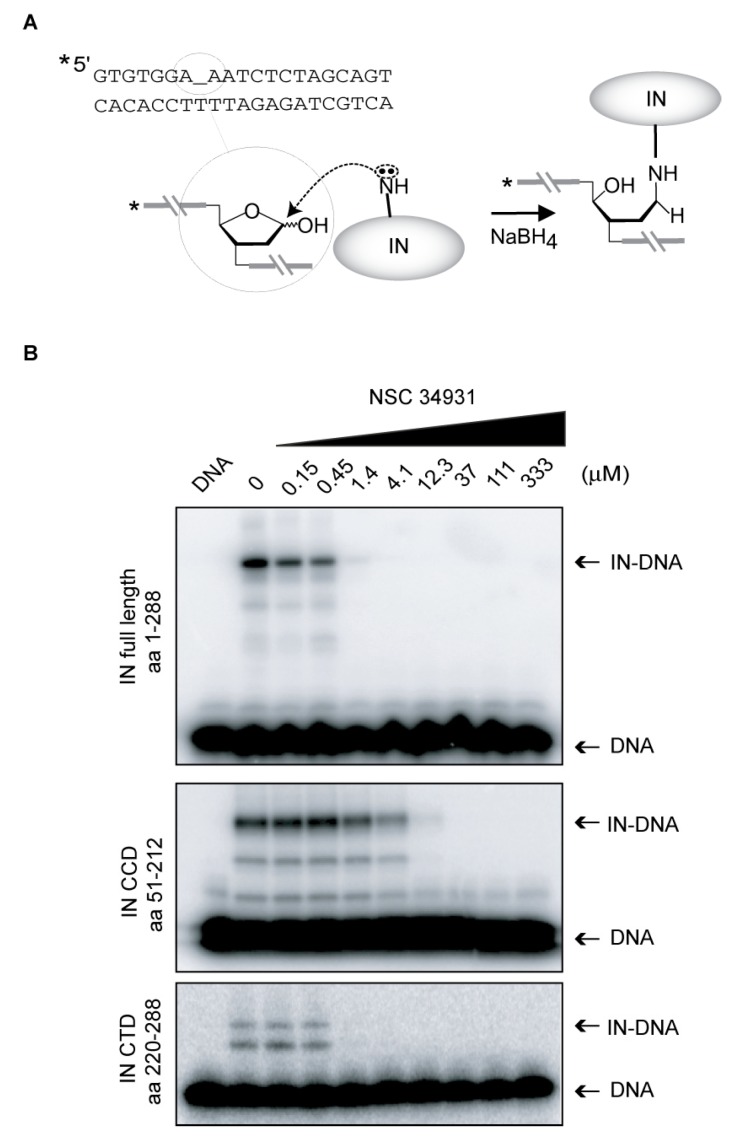
Figure 5.
Inhibition of IN-DNA binding by NSC34931. (A) Principle of the Schiff base crosslinking assay. An abasic site was introduced by uracil DNA glycosylase in the DNA substrate at the -12 position. An IN nitrogen nucleophile (probably lysine) attacks the C1′-carbon of the abasic site. Rearrangement of the initial enzyme–DNA complex leads to the formation of a Schiff base intermediate that can be stabilized by reduction via NaBH4. The asterisk indicates the 5′-[32P]-label. (B) Representative SDS-PAGE image showing the inhibition by NSC34931 of crosslinking between IN and DNA using full-length IN (1–288), the isolated catalytic core domain (CCD) (51–212), or the isolated C-terminal domain (CTD) (220–288).