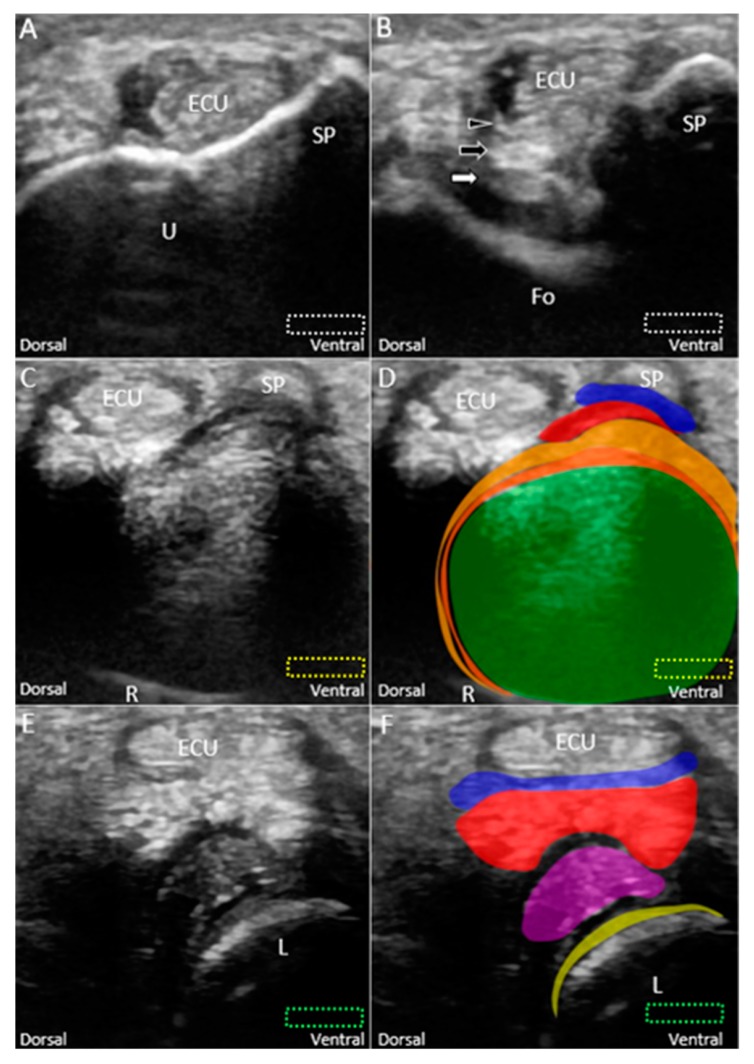
Figure 6.
Imaging of the ulnar fovea using the short-axis approach. (A) The transducer is placed above the ulnar styloid process at first. It is then moved distally and tilted to the cranial aspect. (B) US imaging of the ulnar fovea shows the deep (white arrow) and superficial limbs (black arrow) of the radioulnar ligament and the ulnar collateral ligament (black arrowhead). (C) US and (D) superposed US images of the articular disc above the sigmoid notch of the radius. (E) US and (F) superposed US images of the lunotriquetral ligament and meniscus homologue. The different color dashed rectangles are in accordance with the transducer positions in Figure 3. US: ultrasound; U: ulna; R: radius; L: lunate; SP: styloid process; Fo: fovea; ECU, extensor carpi ulnaris. Articular disc (green shade), radioulnar ligament (brown shade), ulnar collateral ligament (blue shade), lunate cartilage (yellow shade), ulnotriquetral ligament (purple shade), and meniscus homologue (red shade).