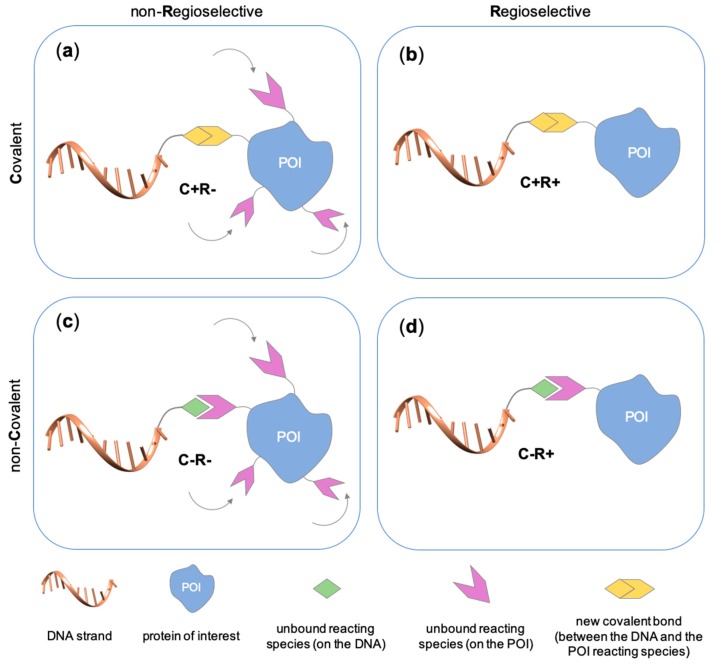
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the chemical methods typically adopted for the synthesis of DNA-protein conjugates. The strategies can be classified according to the establishment of a covalent (C+) or non-covalent (C-) bond between the DNA and protein component as well as on the occurrence (R+) or absence (R-) of regioselectivity. Accordingly, four classes can be distinguished: from (a) to (d), C+R-, C+R+, C-R- and C-R+. The establishment of a covalent bond between the DNA handle (green symbol) and the chemical moiety (magenta symbol) attached to the protein of interest (POI, in blue) gives rise to a new chemical group between the two molecules (yellow symbols merged together). A non-covalent bond instead preserves the identity of the interacting units (green and magenta symbols for the DNA and the POI handles, respectively).