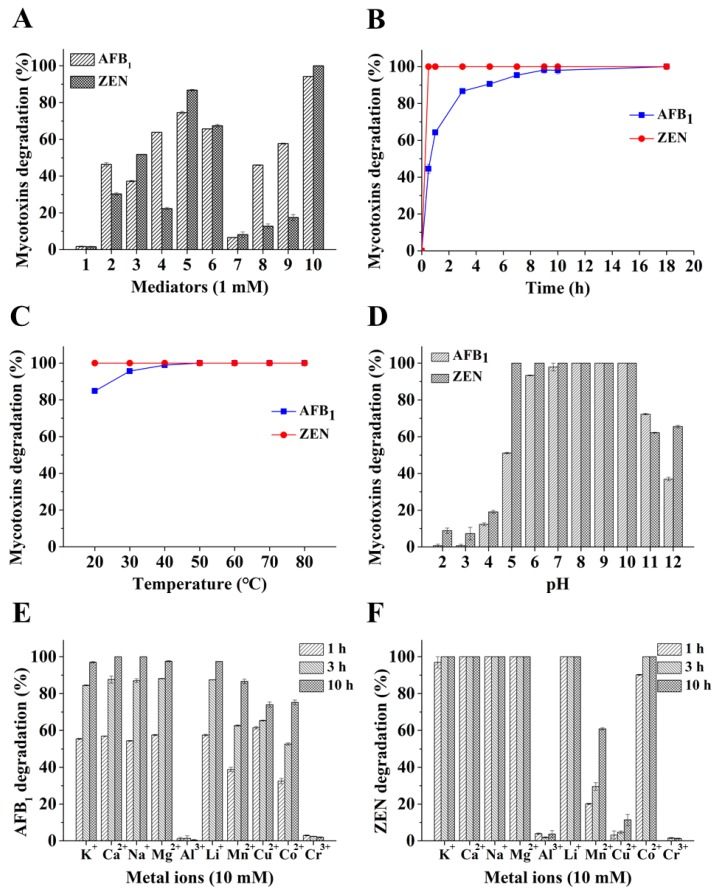
Figure 2.
Screening structurally defined chemical compounds as a mediator of BsCotA in the degradation of Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and zearalenone (ZEN). (A) Identification of structurally defined chemical compounds as effective mediators. AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and one of the mediators (1 mM) in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. The compounds used were: 1, no compound control; 2, p-coumaric acid; 3, syringic acid; 4, vanillin; 5, syringaldehyde; 6, caffeic acid; 7, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HBT); 8. gallic acid; 9, vanillic acid; 10, methyl syringate. (B) Time-course analysis of AFB1 and ZEN transformation by BsCotA in the presence of methyl syringate. AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and 1 mM of methyl syringate in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. The samples were periodically taken for HPLC analysis. Effects of (C) temperature and (D) pH on AFB1 and ZEN transformation by BsCotA in the presence of methyl syringate. For (C), AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and 1 mM of methyl syringate in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at a temperature ranging from 20 to 80 °C for 10 h. For (D), the incubation was carried out in a buffer with the pH ranging from 2.0 to 12.0. Impacts of (E) metal ions on AFB1 and (F) ZEN transformation. AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and 1 mM of methyl syringate in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) and one of the metal ions (10 mM) at 30 °C for 10 h. Each assay was carried out with three independent biological replicates.