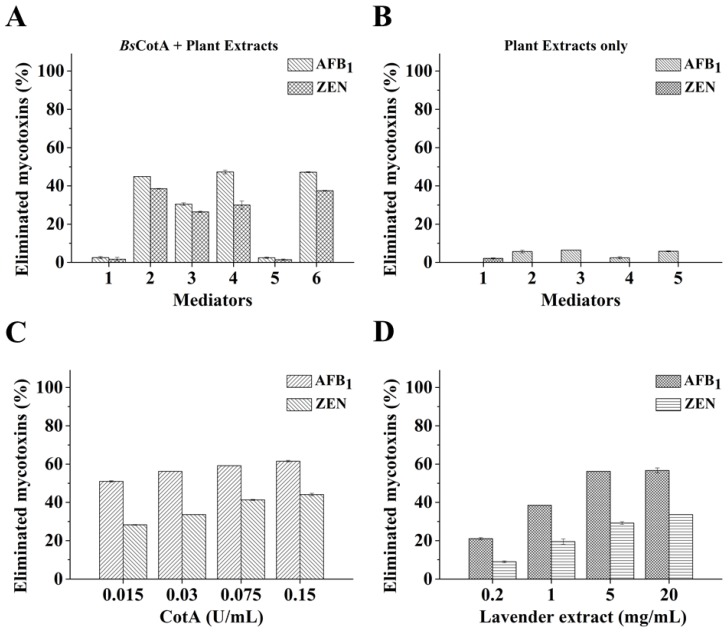
Figure 3.
AFB1 and ZEN degradation by BsCotA using plant extracts as a mediator. (A) Screening of plant extracts as a mediator of BsCotA in AFB1 and ZEN degradation. AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and one of the plant extracts (5 mg/mL) in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. 1, no mediator control; 2, Epimedium brevicornu extract; 3, Cucumis sativus L. extract; 4, Lavandula angustifolia extract; 5, Asparagus officinalis extract; 6, Schizonepeta tenuifolia extract. (B) AFB1 and ZEN incubated only with plant extracts. AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated only with one of the plant extracts (5 mg/mL) in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. 1, E. brevicornu extract; 2, C. sativus L. extract; 3, L. angustifolia extract; 4, A. officinalis extract; 5, S. tenuifolia extract. Effects of (C) BsCotA and (D) L. angustifolia extract concentrations on the transformation rates of AFB1 and ZEN. For (C), AFB1 and ZEN (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with varying concentrations of BsCotA (0.015, 0.03, 0.075, and 0.15 U/mL) and L. angustifolia extract (5 mg/mL) in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. For (D), the two mycotoxins (5 μg/mL each) were individually incubated with BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) and L. angustifolia extract (0.2, 1, 5, and 20 mg/mL) at 30 °C for 10 h. Each assay was carried out with three independent biological replicates.