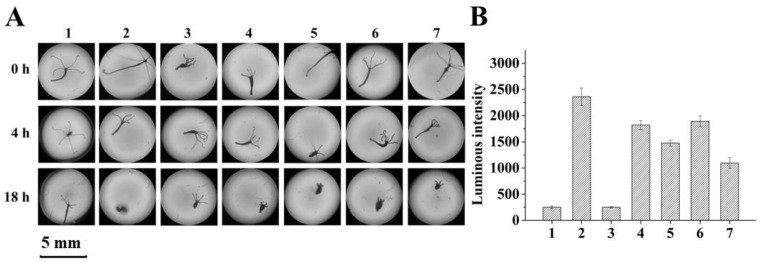
Figure 4.
BsCotA-treated AFB1 and ZEN led to detoxification as determined by using hydra and BLYES yeast as two model systems. (A) Effects of BsCotA treatment on the toxicity of AFB1 to hydra. AFB1 (5 μg/mL) was treated with one of the BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) mediator systems in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. 1, no AFB1 control; 2, untreated AFB1; 3–7, AFB1 treated with one representative structurally defined chemical mediator methyl syringate (3) and four plant extracts with mediating activity, i.e., E. brevicornu extract (4), C. sativus L. extract (5), L. angustifolia extract (6), and S. tenuifolia extract (7). (B) Effects of BsCotA treatment on the estrogenic activity of ZEN to the BLYES yeast. ZEN (5 μg/mL) was treated with one of the BsCotA (0.03 U/mL) mediator systems in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 10 h. 1, no ZEN control; 2, untreated ZEN; 3–7, ZEN treated with methyl syringate (3), E. brevicornu extract (4), C. sativus L. extract (5), L. angustifolia extract (6), and S. tenuifolia extract (7). Each assay was carried out with three independent biological replicates.