Table 1.
The most common antioxidant molecules in neuroprotection and their chemical structure.
| Class of Compounds | Compound Name | Chemical Structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | Vitamin A | retinol |
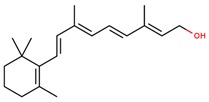
|
|
| retinal |
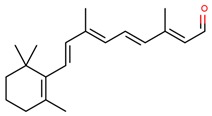
|
|||
| retinoic acid |
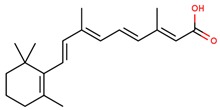
|
|||
| Vitamin E (α-tocopherol) |
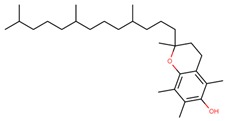
|
|||
| Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) |
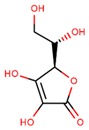
|
|||
| Phenolic compounds | Flavonoids | amurensin |
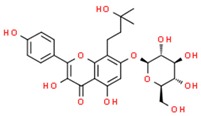
|
|
| cosmosiin |
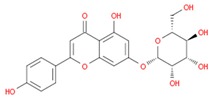
|
|||
| tiliroside |
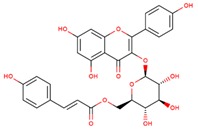
|
|||
| rutin |
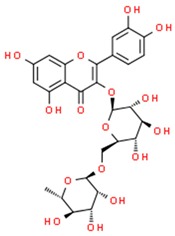
|
|||
| quercetin |
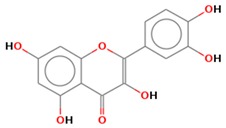
|
|||
| 2′-methoxy-6-methylflavone |
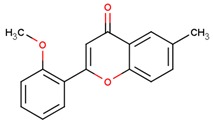
|
|||
| Non-flavonoids | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid |
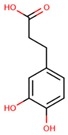
|
||
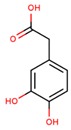
| 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid |
|
|||
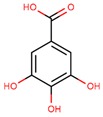
| gallic acid |
|
|||
| ellagic acid |

|
|||
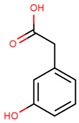
| 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid |
|
|||
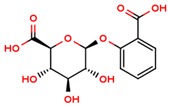
| salicylic β-d-O-glucuronide |
|
|||
| carnosic acid |
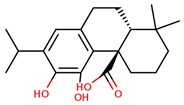
|
|||
| rosmarinic acid |
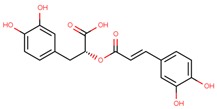
|
|||
| Carotenoids | α-carotene |
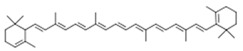
|
||
| β-carotene |
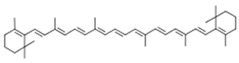
|
|||
| lycopene |
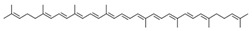
|
|||
| lutein |
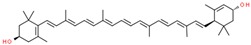
|
|||
| cryptoxanthin |
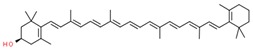
|
|||
