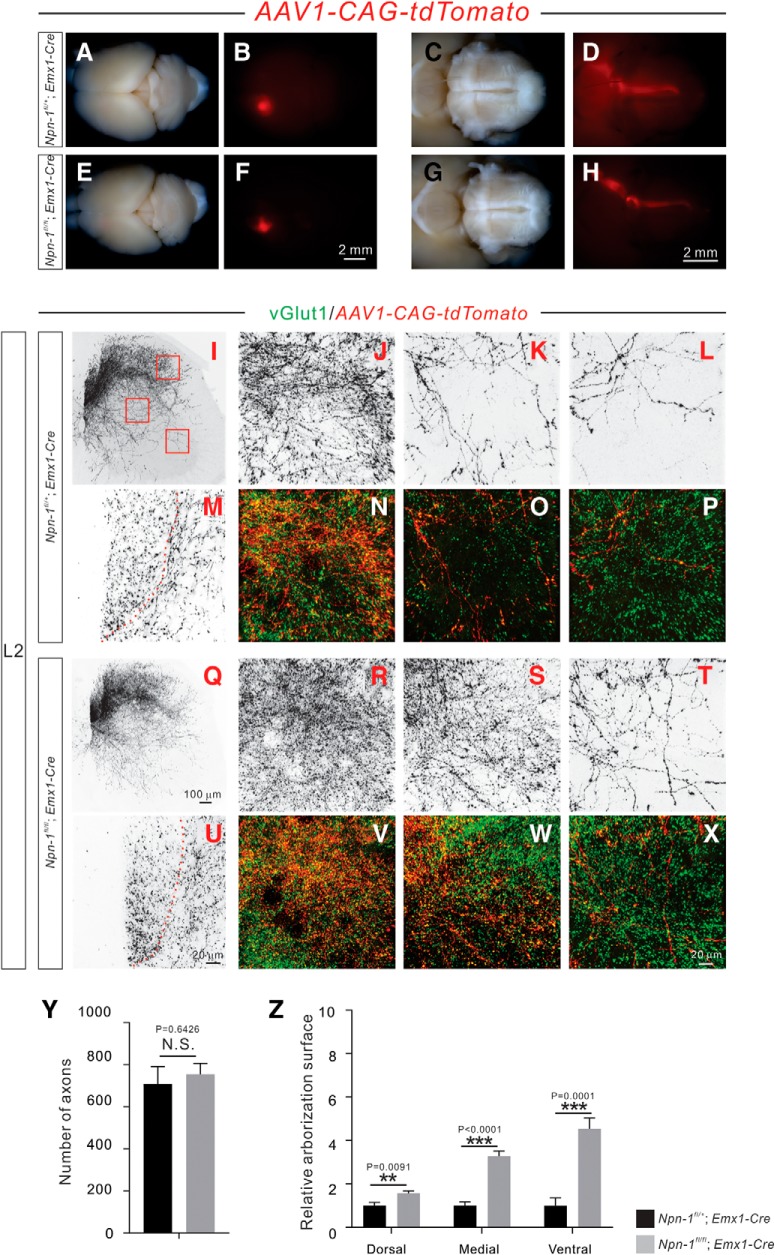
Figure 5.
Adult Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre mice display exuberant CS axon branches. A–H, Anterograde tracing strategy to label unilateral CSNs and their descending axons. Top views of the brain show the cortical neurons that were labeled by AAV1-CAG-tdTomato in 6 week-old Npn-1fl/+; Emx1-Cre (A, B; n = 6) and Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre (E, F; n = 7) mice. Ventral views of the brainstem show CS axons labeled by tdTomato in Npn-1fl/+; Emx1-Cre (C, D) and Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre (G, H) mice. The overall morphologies of CS axons in Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre and control mice were similar. I–X, Immunofluorescent labeling of lumbar spinal cord sections using antibodies targeting tdTomato (red; shown in black except in N–P, V–X) and vGlut1 (green). Transverse views show the CS innervation of the lumbar spinal cord by unilateral CS axons and their collaterals labeled by tdTomato in Npn-1fl/+; Emx1-Cre (I–P) and Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre (Q–X) mice. Low-magnification views (I, Q) show CS innervation of the lumbar spinal cord. High-magnification views (M, U) of the dorsal funiculus show individual CS axons labeled by tdTomato. The dorsal (J, N, R, V), medial (K, O, S, W), and ventral (L, P, T, X) spinal cord (high-magnification views from Fig. 5I,Q), showing exuberant CS axon branches in Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre mice. CS boutons labeled by tdTomato were colocalized with the presynaptic marker vGlut1. Y, Quantification of tdTomato-labeled CS axons showing similar (p = 0.6426) numbers between mutant and control mice. Z, Quantification of axon collateral intensities showing that Npn-1fl/fl; Emx1-Cre mice had significantly more axon collaterals in the dorsal (p = 0.0091), medial (p < 0.0001), and ventral (p = 0.0001) regions of the lumbar spinal cord compared with Npn-1fl/+; Emx1-Cre mice. Scale bars: F, H, 2 mm; Q, 100 μm; U, X, 20 μm.