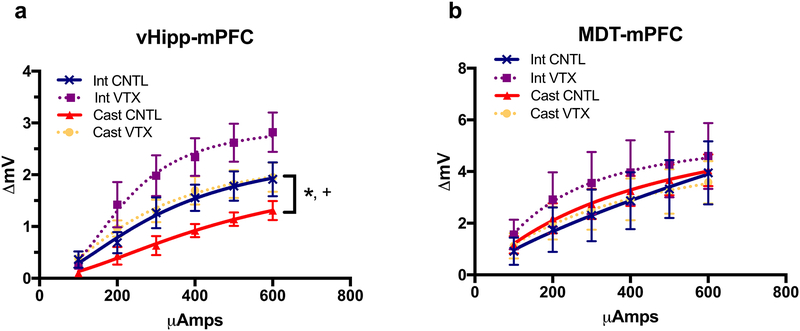
Fig. 3.
Changes in responsivity of the mPFC to stimulation of excitatory afferent input from the vHipp but not the MDT after castration and vortioxetine. a Castrated male rats treated with control chow exhibited an attenuated electrical response in the mPFC evoked by stimulating the excitatory afferent input from the vHipp, compared to intact rats treated with control diet (*p<0.05). Chronic dietary vortioxetine (2 weeks, 28 mg/kg/day) normalized the evoked response of castrated male rats to a level comparable to that seen in intact control rats (+p<0.05). Note that vortioxetine alone increased the response in intact controls. n=6–8 per group. b There was no difference in electrical response in the mPFC evoked by stimulating the excitatory afferent input from the MDT. All data are presented as mean ± SEM, n=7–9 per group.