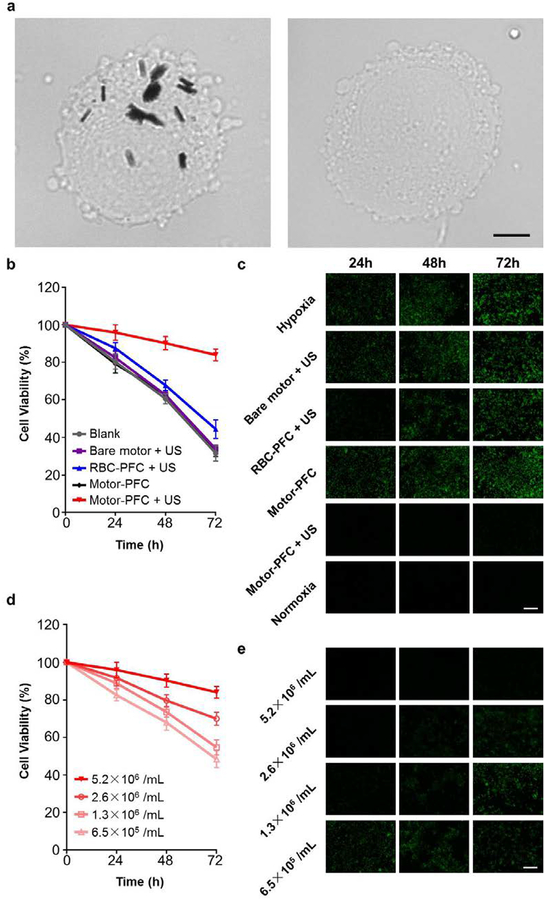
Figure 5. Intracellular oxygen delivery using acoustically-propelled Motor-PFC.
(a) Motor-PFC internalization into J774 cells treated with 5 min US (left) or without US (right); cells imaged under optical microscope. Scale bars, 5 μm. (b) Viability of J774 cells after incubation with different treatment conditions and then being subjected to hypoxia. Cells were incubated under hypoxic conditions for 24, 48, or 72 h, and then normalized to corresponding viability in normoxia (n=4, mean ± s.d.). (c) Fluorescence microscopy of J774 cells after incubation with different treatment conditions and then being subjected to hypoxia. Cells were labeled with Image-iT Green hypoxia reagent (green) for visualization. Images taken at 24, 48, and 72 h. Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Viability of J774 cells after incubation with Motor-PFC at different input concentrations and then being subjected to hypoxia. Cells were incubated under hypoxic conditions for 24, 48, or 72 h, and then normalized to corresponding viability in normoxia (n=4, mean ± s.d.). (e) Fluorescence microscopy of J774 cells after incubation with Motor-PFC at different input concentrations and then being subjected to hypoxia. Cells were labeled with Image-iT Green hypoxia reagent (green) for visualization. Images taken at 24, 48, and 72 h. Scale bar, 100 μm.