Figure 3. Sleep fragmentation disrupts learning.
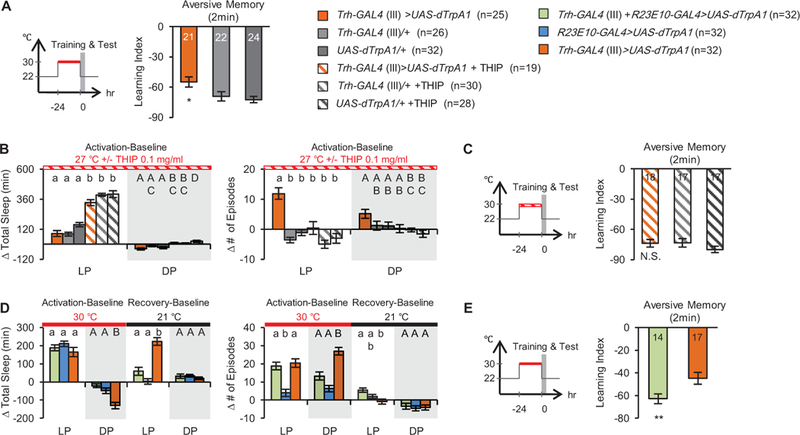
(A) Activation of Trh-GAL4+ neurons for 24 h (red bar) before training and testing disrupts aversive olfactory learning. Schematic of experiment is shown at left, data for 2 min memory at right. (B) Effects of 0.1 mg/ml THIP on the change in total sleep and episode number relative to baseline day. Statistically similar LP (lower case) and DP (upper case) groups are marked by the same letter; different letters indicate significant differences (p<0.05) between groups. (C) Application of THIP while Trh-GAL4+ neurons were activated (red striped bar) rescues learning. Schematic of experiment is shown at left. (D) Effects of co-activation of dorsal fan-shaped body and Trh-GAL4+ neurons on sleep. (E) Co-activation of dorsal fan-shaped body with Trh-GAL4+ neurons (red bar) rescues learning. For panels A, C and E, the number of independent reciprocal experiments is indicated on the bars. See also Figure S3.
