Figure 4. Serotonergic signaling to the EB regulates sleep structure via 5HT7Rs.
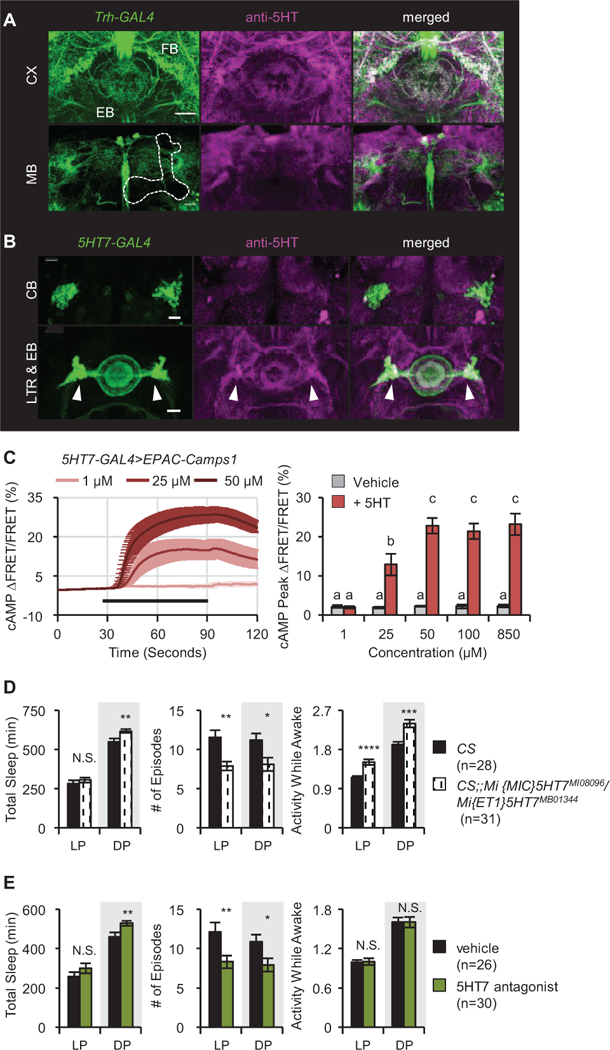
(A) Expression pattern of TrH(III)>GFP (green) costained with anti-5HT (magenta). Upper panels show sections at the level of the central complex (CX); lower panels the level of the mushroom body (MB, outlined). FB, fan-shaped body; EB, ellipsoid body. (B) Expression pattern of 5HT7>GFP (green) with anti-5HT (magenta). Upper panels, EB cell bodies (CB), lower panels, EB processes and lateral triangle region (LTR, white arrowheads) where serotonergic inputs enter. Scale bar = 20 μm for all images. (C) 5HT7-GAL4+ neurons in the EB respond to 5HT. Left: cAMP levels after application of 5HT (black bar) in the presence of 1 μM TTX. n = 8–9 for all groups. Right: quantified data compared to vehicle. (D) 5HT7R mutants exhibit more consolidated sleep in both the day (LP) and the night (DP) as well as increased nighttime sleep and mild hyperactivity. (E) Feeding of the 5HT7 antagonist (SB258719) to wild type flies consolidates sleep. Activity while awake is not affected. Data are shown for Day 4 of drug application. See also Figure S7.
