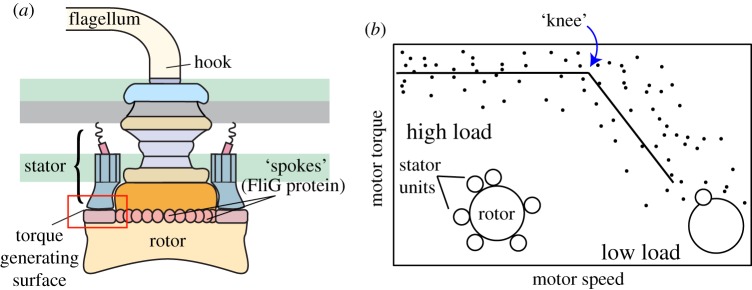
Figure 1.
BFM structure and dynamics. (a) The flagellar motor’s rotor consists of a series of large co-axial rings that attach to a flagellar filament via a flexible hook. An active motor can have up to at least 11 torque-generating stator complexes. Stators interact with proteins (FliG) along the rotor’s edge to drive motor rotation. (b) Experiments in recent years have established that the number of torque-generating units varies with external load on the motor (among other possible factors, including IMF). Points in the high-load regime correspond to motors near full occupancy and points at low loads to motors with only one or two. Data shown from [5]. Solid lines are included to guide the eye. (Online version in colour.)