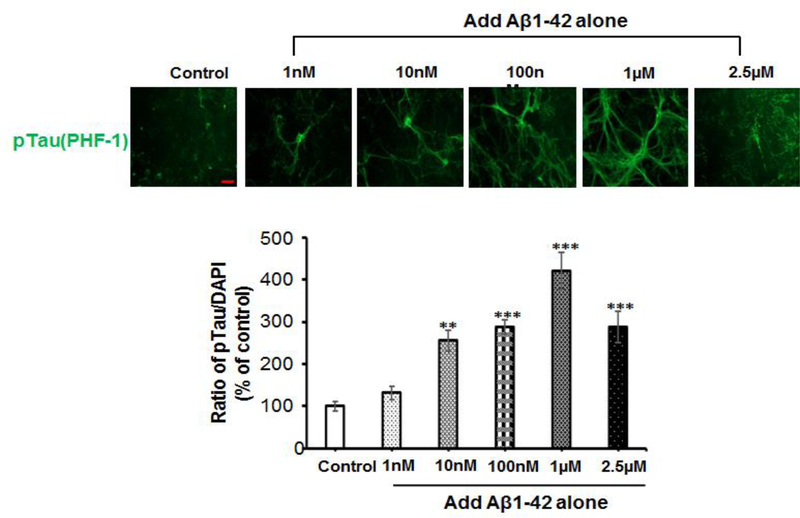
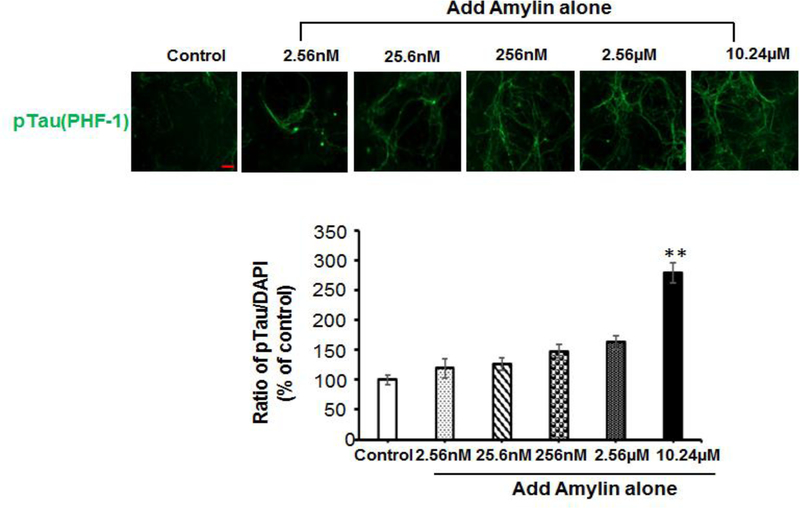
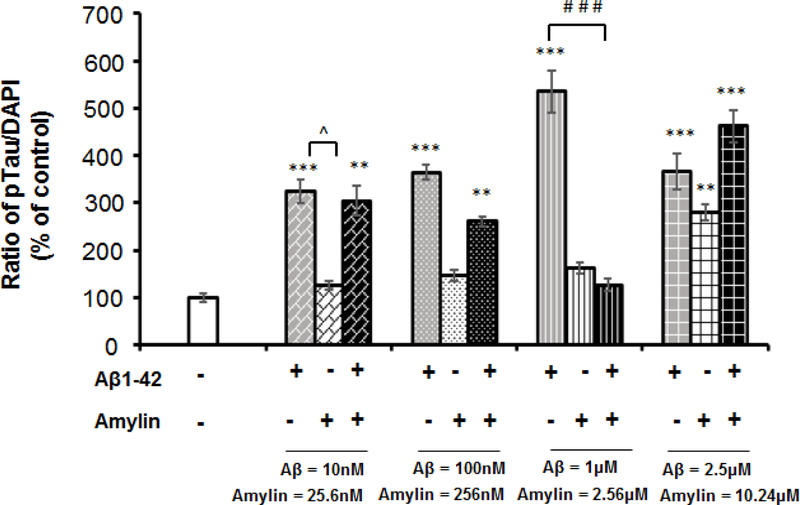
Figure 2. Either Aβ or amylin alone could induce cellular tau phosphorylation in primary neurons.
Mouse cortical neurons were grown and treated with Aβ1–42 alone (A), or human amylin alone (B), or Aβ1–42 plus amylin (C). The neurons were fixed, incubated with the pTau antibody, PHF-1. When the concentration of either peptide was increased, both Aβ1–42 (A) and human amylin (B) alone induced cellular tau phosphorylation (pTau) (Scale bars: 50 μm). The maximum amount of 2.5 μM Aβ1–42 induced less pTau than 1 μM Aβ1–42 due to some neuronal death. The level of tau phosphorylation was normalized by DAPI to allow comparisons among different experimental groups. Values are expressed relative to the controls (untreated mouse primary neurons), which were set as 100%. Values are the mean ± SE from all experiments. For A and B, compared to the control condition, differences with statistical significance are shown with * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001. For C, compared to the condition of Aβ1–42 alone, the differences of condition of amylin plus Aβ1–42 are shown with statistical significance # p<0.05; ## p<0.01; the differences between the conditions with amylin alone and amylin plus Aβ1–42 are shown with statistical significance ^ p<0.05; ^^ p<0.01. Each experiment was repeated three times and the representative imagings are shown.