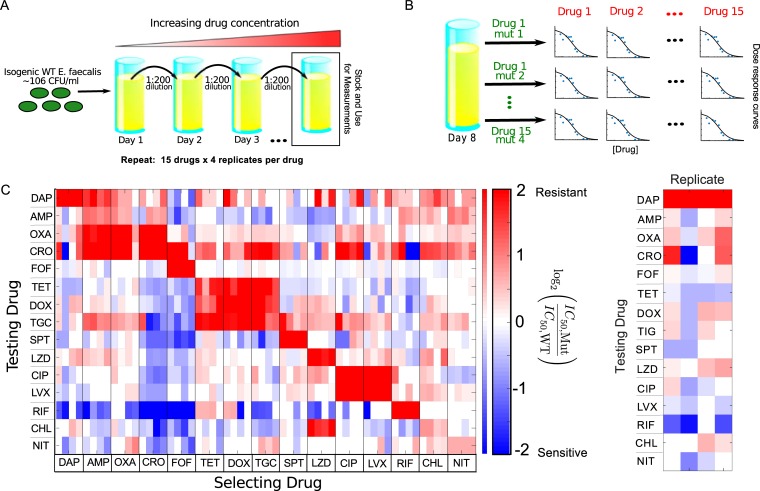
Fig 1. Collateral effects are pervasive and vary across parallel evolution experiments in E. faecalis.
(A) E. faecalis strain V583 was exposed to increasing concentrations of a single antibiotic over an 8-day serial-passage experiment with daily 200-fold dilutions (maximum of 60 generations total; see Materials and methods). The evolution was performed in quadruplicate for each drug and repeated for a total of 15 drugs (Table 1). After 8 days, a single mutant was isolated from each population. (B) The IC50 for each of 15 drugs was estimated for all 60 mutants by nonlinear fitting of a dose-response curve (relative OD) to a Hill-like function (Materials and methods). (C) Main panel: resistance (red) or sensitivity (blue) of each evolved mutant (horizontal axis; 15 drugs × 4 mutants per drug) to each drug (vertical axis) is quantified by the log2-transformed relative increase in the IC50 of the testing drug relative to that of WT (V583) cells. Although the color scale ranges from a 4× decrease to a 4× increase in IC50, it should be noted that both resistance to the selecting drug (diagonal blocks) and collateral effects can be significantly higher. Each column of the heat map represents a collateral sensitivity profile for one mutant. Right panel: enlarged first column from main panel. Mutants isolated from replicate populations evolved to DAP exhibit diverse sensitivity profiles. Although all mutants are resistant to the selecting drug (DAP), mutants may exhibit either sensitivity or resistance to other drugs. For example, the first and last replicates exhibit cross-resistance to CRO, whereas replicate 2 exhibits collateral sensitivity, and replicate 3 shows little effect. Data underlying this figure can be found in S1 Data. AMP, ampicillin; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CRO, ceftriaxone; DAP, daptomycin; DOX, doxycycline; FOF, fosfomycin; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration; LVX, levofloxacin; LZD, linezolid; mut, mutant; NIT, nitrofurantoin; OD, optical density; OXA, oxacillin; RIF, rifampicin; SPT, spectinomycin; TET, tetracycline; TGC, tigecycline; WT, wild-type.