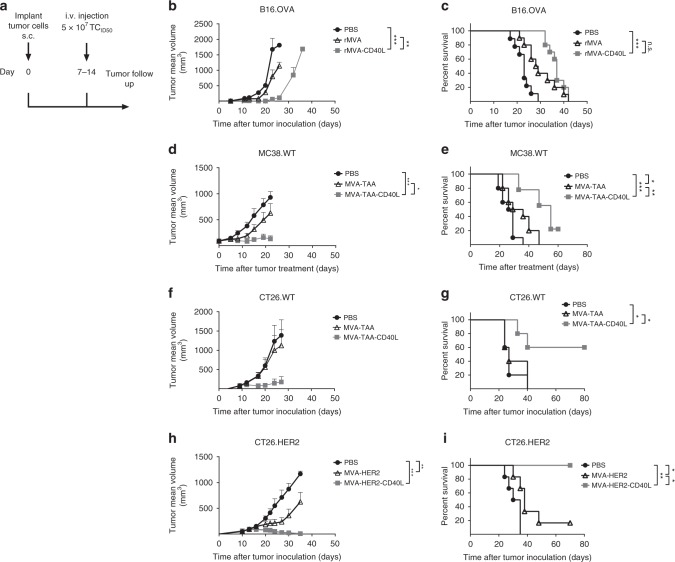
Fig. 1.
Therapeutic efficacy of rMVA-CD40L in unrelated, large, established tumor models. a Experimental layout: briefly, C57BL/6 (b–e) or Balb/c mice (f–i) received either B16.OVA (b, c), MC38.WT (d, e), CT26.WT (f, g) or CT26.HER2 (h, i) cells subcutaneously in the flank. Seven to 14 days later, when tumors were above 60 mm3, mice were immunized intravenously either with PBS or with 5 × 107 TCID50 of the mentioned rMVA viruses. b, c B16.OVA; b tumor size follow-up (n = 5 mice/group) and c overall survival (n = 10 mice/group) of mice injected either with PBS, MVA-OVA, or MVA-OVA-CD40L; d, e MC38.WT tumor-bearing mice were grouped 18 days after tumor cell inoculation, when tumors were above 90 mm3; d tumor size follow-up (n = 10 mice/group) and e overall survival (n = 10 mice/group) of mice injected either with PBS, MVA-TAA, or MVA-TAA-CD40L until day 60 after treatment; f, g CT26.WT; f tumor size follow-up (n = 5 mice/group), and g overall survival (n = 5 mice/group) of mice injected either with PBS, MVA-TAA, or MVA-TAA-CD40L; h, i CT26.HER2; h tumor size follow-up (n = 6 mice/group), and i overall survival (n = 6 mice/group) of mice injected either with PBS or MVA-HER2-CD40L. b, d, f, and h Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Panel b is representative of at least two independent experiments. Panel c represents overall survival of two merged independent experiments. The antitumor efficacy of MVA-HER2-CD40L in h and i has been tested in the CT26.HER2 tumor model in at least two independent experiments. One-way ANOVA at day 20 after tumor inoculation was performed on b, d, f, and h. Log-rank test on mouse survival was performed for c, e, g, and i. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005