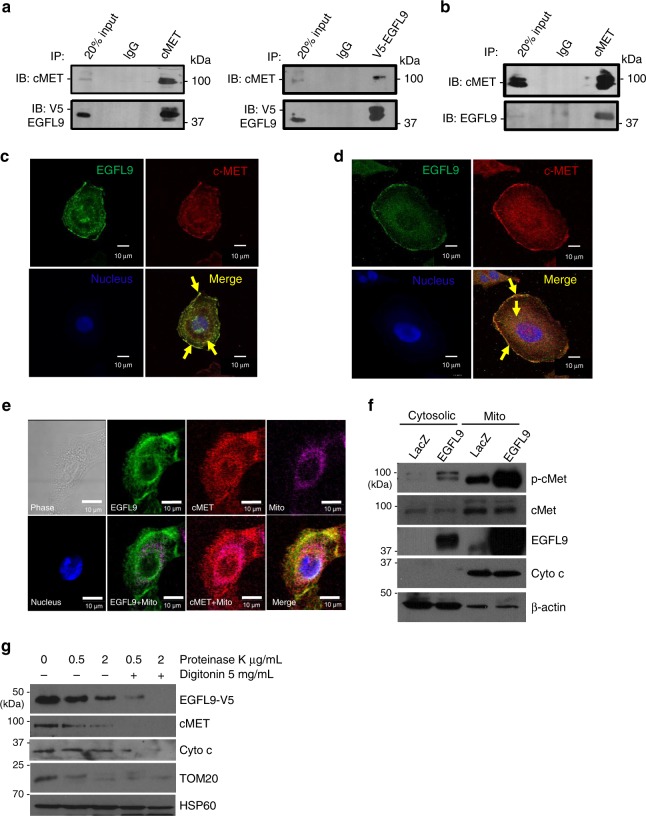
Fig. 6.
Physical association and co-localization of EGFL9 and cMET. a Interaction of EGFL9 and cMET in HMLE/EGFL9 cells. Left panel: immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-v5 antibody followed by immunoblotting with cMET antibody. Right panel: immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-cMET followed by immunoblotting with anti-V5 antibody. b Interaction of EGFL9 and cMET in SUM159 cells. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-cMET antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-EGFL9 antibody. For both a and b, IgG was used as the IP-control. c, d Subcellular co-localization of EGFL9 and cMET in HMLE/EGFL9 (c) and SUM159 (d) cells. The distribution of ectopic expressed EGFL9 was detected with anti-v5 antibody (c). Endogenous EGFL9 was detected by EGFL9 antibody (d). cMET was detected with anti-cMET antibody (c, d). DAPI staining was included to visualize the cell nucleus. Scale bar: 10 µm. e Co-localization of EGFL9 and cMET in mitochondria in HMLE/EGFL9 cells. Mitochondria were stained with Mitotracker deep-red dye. The distribution of ectopic expressed EGFL9 was detected with an anti-V5 antibody. cMET was detected with an anti-cMET antibody. DAPI staining was included to visualize the cell nucleus. Scale bar: 10 µm. f Cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were isolated from HMLE/EGFL9 cells and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by probing with specific antibodies as indicated. Cyt c, mitochondrial marker; β-actin, cytosolic marker. g Proteinase K protection assay. Equal amounts of purified mitochondria were treated as indicated. Lysed protein was separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies