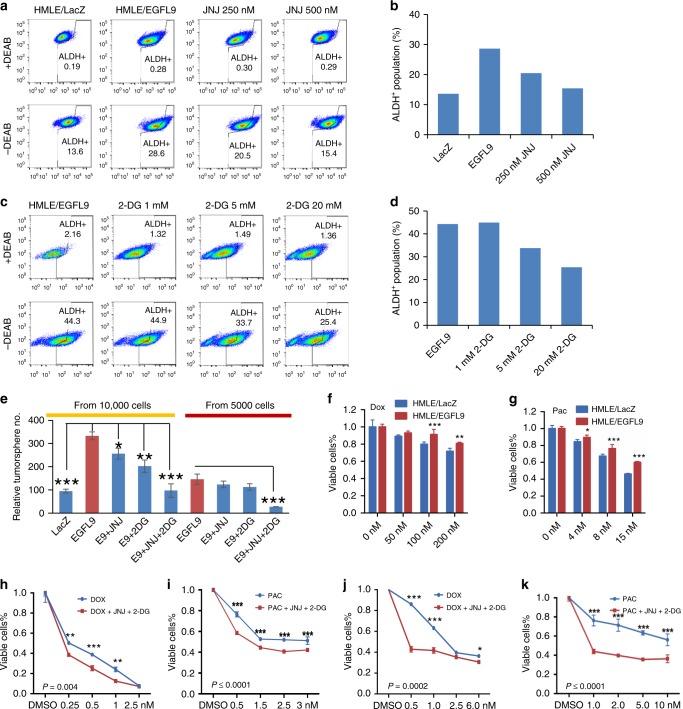
Fig. 8.
EGFL9 induces stemness in mammary epithelial cell. a ALDH+ FACS profiles are shown for HMLE/LacZ cells, and HMLE/EGFL9 cells with different doses of JNJ38877605 treatment. b Summary of percentage of ALDH+ cells in HMLE cells with EGFL9 expression and 250 and 500 nM of JNJ38877605 treatment. c ALDH+ FACS profiles are shown for HMLE/LacZ cells, and HMLE/EGFL9 cells with different doses of 2-DG treatment. d FACS analysis of the ALDH+ fraction cells in HMLE cells with EGFL9 expression and 5 and 20 mM of 2-DG treatment. e Tumorsphere formation assay of HMLE/EGFL9 (1 × 104 and 0.5 × 104) cells with JNJ38877605 and/or 2-DG treatment. f, g The effect of EGFL9 on drug resistance in HMLE cells. Different doses of Dox (f) and Pac (g) were used to treat HMLE/LacZ and HMLE/EGFL9 cells. MTT assay was used to measured cell viability. For panels from e to g, each bar represents the mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean of a representative experiment performed in triplicate). P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. h, i Treatment of JNJ38877605 (500 nM) and 2-DG (5 mM) in combination sensitizes HMLE/EGFL9 cells to Dox (h) and Pac (i) treatment. j, k Treatment of JNJ38877605 (500 nM) and 2-DG (5 mM) in combination sensitize SUM159 cells to Dox (j) and Pac (k) treatment. For panels from h to k, two-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparisons was used to compare the two values at a given concentration. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001