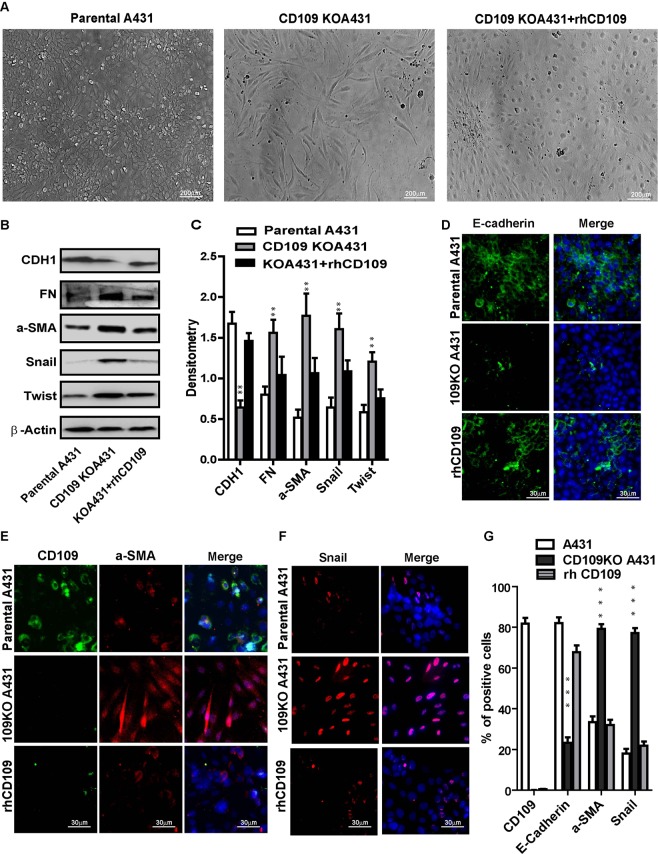
Figure 7.
rhCD109 rescue the EMT phenotype of CD109-KO SCC cells. (A) Phase contrast microscopy for the morphology of parental A431 cells (Left), CD109-KO A431 cells (Middle), and CD109-KO cells treated with rhCD109 protein (Right), demonstrated that rhCD109 rescued the epithelial phenotype of CD109-KO cells. (B) Western blot detection and (C) quantification of E-Cadherin (CHD1), fibronectin (FN), alpha-smooth muscle actin (a-SMA), Snail and Twist. The treatment of rhCD109 protein rescue E-cadherin expression and significantly suppressed the expressions of mesenchymal proteins and EMT markers. (D–F) Representative Immunofluorescence microscopy images and (G) quantification for CDH1 (green, D), a-SMA (red, E), Snail (red, F) and DAPI (blue) in parental A431 cells, CD109 KO cells, and CD109-KO cells treated with rhCD109 as indicated, confirming that the treatment of CD109 suppressed EMT markers and rescued the epithelial traits in CD109-KO cells. All the results are expressed as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. Significance is calculated using a One-Way ANOVA *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. Scale bars: 20,30 and 200 μm in low and high magnification, as indicated.