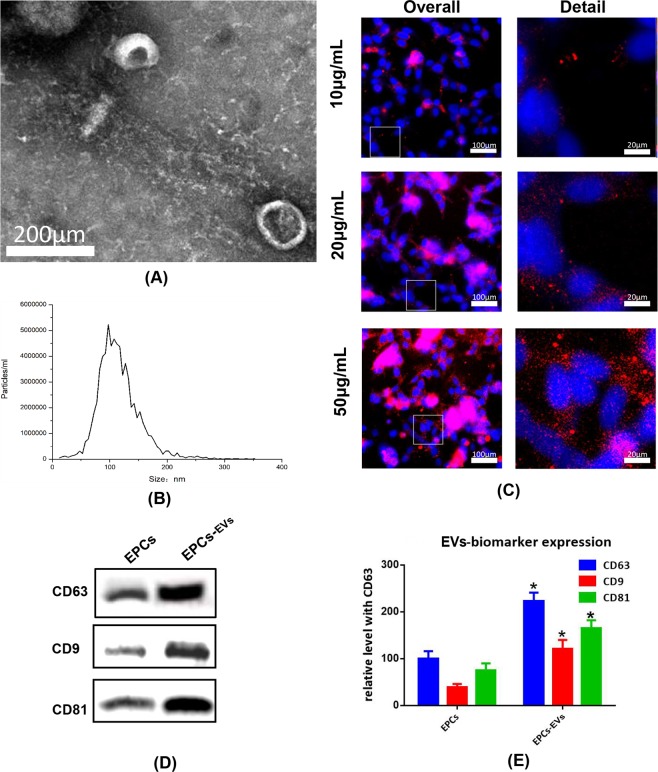
Figure 2.
Identification and internalization of EPC-EVs. Extracellular vesicles were isolated from samples with an extracellular vesicle isolation kit from mouse osteoblast medium after specific experimental treatments. (A) Morphological features of extracellular vesicles were observed via bio-transmission electron microscopy. (B) Particle size of extracellular vesicles was detected with NTA. The X-axis shows the particle size inside of the sample, and the Y-axis shows the concentration of particles with a certain size. Total protein was extracted from extracellular vesicles and analysed with western blotting. Representative images (D,E) histograms showing the expression levels of CD9, CD63, and CD81, which are surface markers of extracellular vesicles. PKH26-labelled extracellular vesicles at 10, 20, 50 µg/mL (approximately 0.69 × 1010, 1.38 × 1010 and 3.45 × 1010 vesicles) were co-cultured with mouse osteoblasts for 3 hours. (C) Immunofluorescence images show the uptake of extracellular vesicles by osteoblasts. The nucleus was labelled with DAPI (blue), and PKH26-labelled extracellular vesicles were internalized by osteoblasts (red).