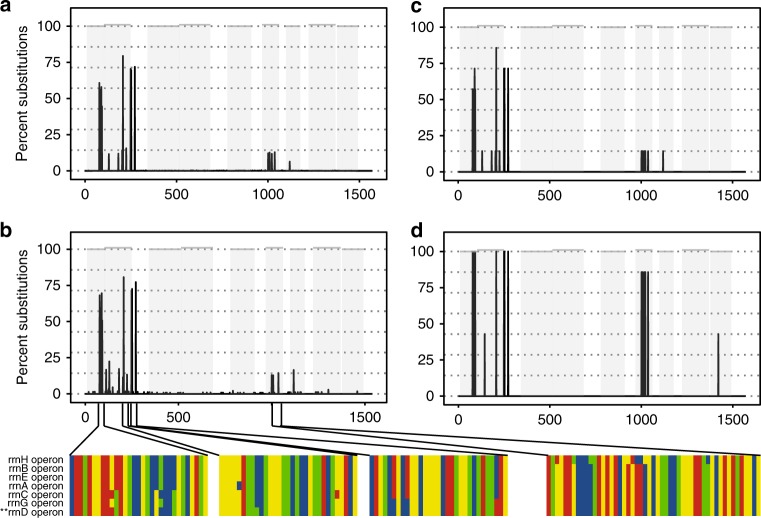
Fig. 2.
Polymorphisms in E. coli 16S rRNA gene sequences. a The position and frequency of substitutions appearing in E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 V1–V9 amplicons generated from our mock community and sequenced on the PacBio RS II platform. b The position and frequency of substitutions in reads generated from genomic sequencing of the isolated E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Magnified regions show respective positions in the alignment of all seven 16S genes present in the E. coli K-12 MG1655 reference genome. The 16S sequence from the rrnD operon (**) is used as the reference for all SNP phasing. c The predicted nucleotide substitution profile of E. coli K-12 MG1655 based on aligning the seven 16S gene sequences present in the reference genome. d The predicted substitution profile of E. coli O157 Sakai based on aligning the seven 16S gene sequences present in the reference genome. Gray panels depict variable regions defined by commonly used primer-binding sites (Supplementary Table 1). Dashed lines indicate the expected proportion of nucleotide substitutions, given there are seven 16S gene copies within each genome. Source data are provided as a Source Data file