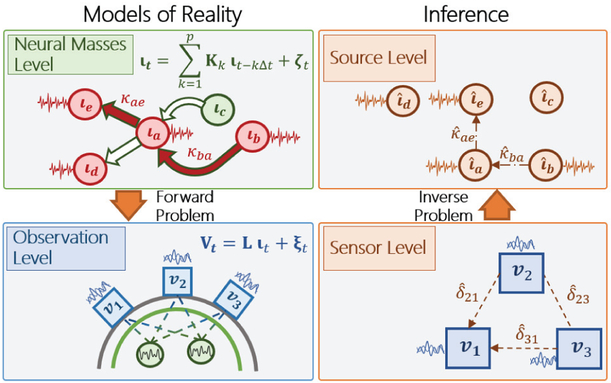
Fig. 1.
Levels involved in estimating neural connectivity from EEG and MEG. On the left models of brain reality. On the right, inferences made about this reality. Identifying neural connectivity is the ultimate objective. This is defined by the interactions (κ) between the activities of neural sources (ι). These in turn, determine the observed time series (ν) at the sensors. From these time series one can obtain measures of statistical dependence (δ). The attempt to use δ as a proxy for κ is known as “sensor level connectivity”. “Source level connectivity” solves the inverse problem to estimate κ. Estimated quantities at sensor and source levels are denoted as , , .