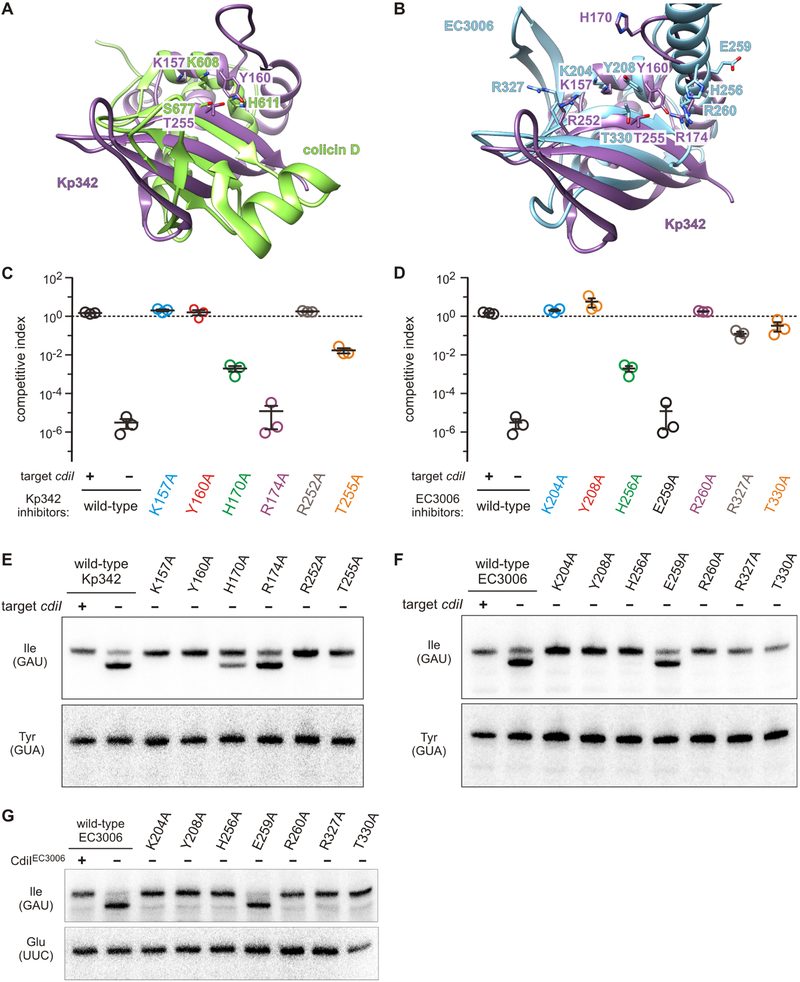
Figure 7. The nuclease active sites of CdiA-CTKp342 and CdiA-CTEC3006.
A) Superimposition of CdiA-CTKp342 onto the nuclease domain of colicin D. B) Putative active sites of CdiA-CTKp342 and CdiA-CTEC3006 nuclease domains. C & D) Competition co-cultures. Target bacteria were co-cultured at a 1:1 ratio with inhibitor cells that deliver the indicated CdiA-CTKp342 (panel C) or CdiA-CTEC3006 (panel D) variants. Competitive indices are calculated as the ratio of viable target to inhibitor cells at 1 h divided by the initial ratio. Data are from three independent experiments together with the average ± SEM. See also Figure S4. E & F) Toxin activities in co-cultures. Inhibitor strains were co-cultured with the indicated target cells for 30 min, then total RNA was isolated for Northern blot analysis. G) In vitro nuclease activity of CdiA-CTEC3006 variants. The indicated CdiA-CTEC3006 domains were purified and incubated with deacylated tRNA substrate.