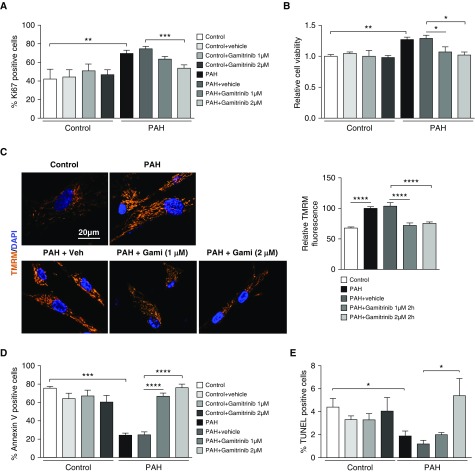
Figure 5.
Selective mitochondrial HSP90 inhibition reduces pulmonary arterial hypertension–pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PAH-PASMC) proliferation and resistance to apoptosis without affecting control PASMCs. (A) Proliferation (Ki67) was measured in control PASMCs and PAH-PASMCs treated or not with Gamitrinib or its vehicle (DMSO) for 48 hours. The graph shows the percentage of cells with positive nuclear staining. PAH-PASMCs exhibit a significantly greater proliferation rate than control cells. Gamitrinib reduces PAH-PASMC proliferation without affecting control cells. (B) Cell viability was examined by thiazolyl blue tetrazolium blue assay. (C) Representative images and corresponding quantitative analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential in cells exposed or not to Gamitrinib or its vehicle (DMSO) for 2 hours, detected by tetramethylrhodamine, methyl ester fluorescence. Gamitrinib depolarizes PAH-PASMC mitochondria. (D and E) Apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin V and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assays. PAH-PASMCs are more resistant to starvation-induced apoptosis (0 and 1% fetal bovine serum) than control PASMCs. Gamitrinib induces apoptosis in PAH-PASMCs without affecting control cells. Experiments were performed in three control and four PAH-PASMC cell lines. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Gami = Gamitrinib; TMRM = tetramethylrhodamine, methyl ester; Veh = vehicle.