Figure 5.
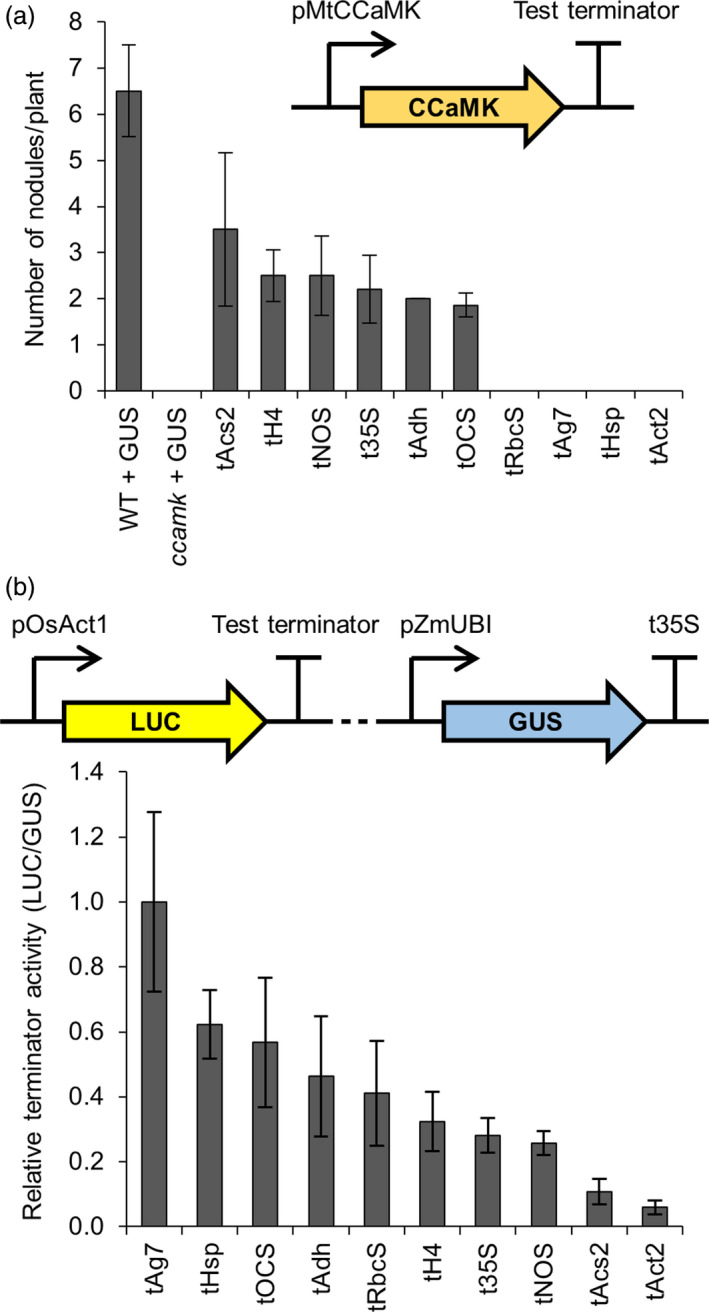
Terminators from the standard genetic parts library show varying levels of functionality in different plant species. (a) Constructs containing terminators from the standard genetic parts library terminating expression of the CCaMK gene (inset) were transformed into Medicago truncatula ccamk‐1 mutant plants via Agrobacterium rhizogenes‐mediated transformation. The numbers of root nodules on these plants were counted three weeks after inoculation with Sinorhizobium meliloti. Data represent mean ± standard error. An average of 9 independently transformed M. truncatula plants were assessed per construct (dsRED in the T‐DNA confirmed transformation). Control wild‐type (WT) and ccamk mutant plants were transformed with a pAtUBI10‐GUS construct (GUS). (b) Multigene constructs containing terminators from the standard genetic parts library driving expression of the firefly luciferase (LUC) reporter gene, plus a constitutively expressed β‐glucuronidase gene (GUS; see figure inset), were expressed in barley (T0 roots). GUS and LUC reporter gene activities were quantified using a plate reader, and terminator activity was calculated by determining the LUC to GUS ratio (with normalization to tAg7 terminator). Data represent mean ± standard error. An average of 5 T0 barley root samples with transgene copy numbers varying between 1 and 4 were assessed per construct. Dotted line in figure inset represents 3.6 kb of plasmid sequence that was unchanged between constructs containing different test terminators. Terminators tRbcS, tAg7, tHsp and tAct2 showed no ccamk‐1 mutant complementation.
