Figure 6.
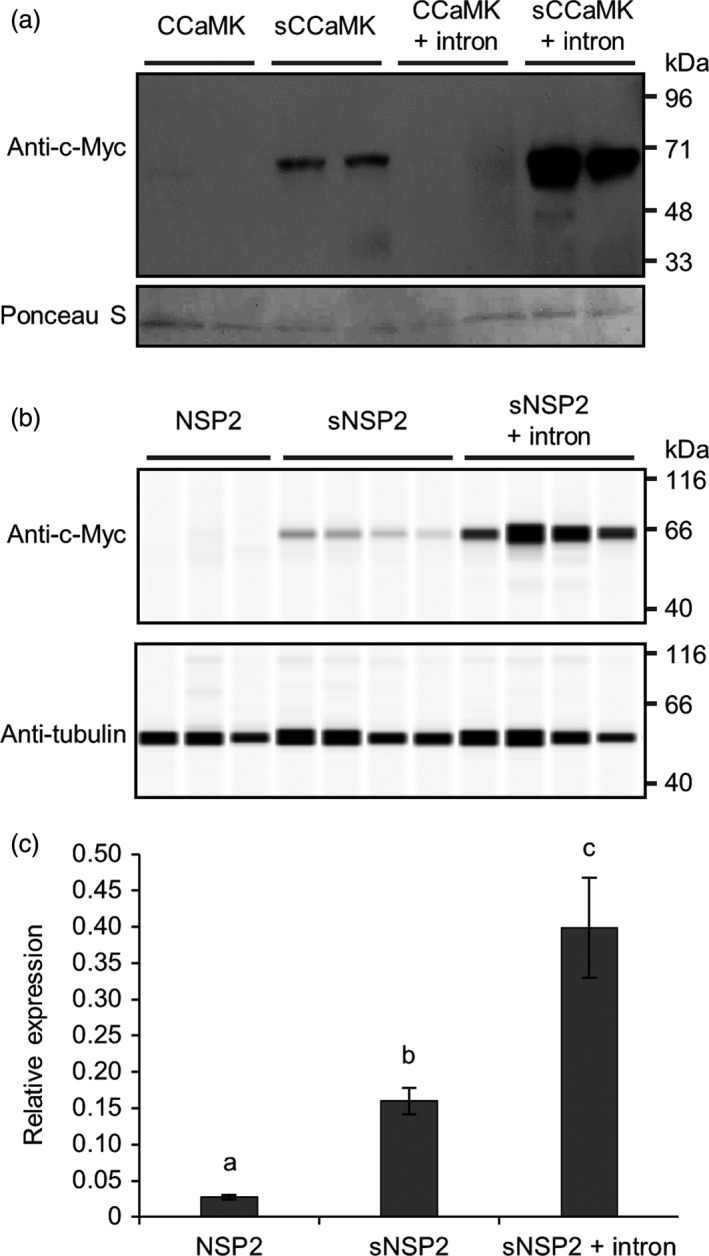
Codon optimization and intron‐mediated enhancement increase transgene expression in barley. (a) Total protein was extracted from T1 barley plants transformed with constructs over‐expressing different versions of Medicago truncatula CCaMK tagged with an N‐terminal 3xMyc tag. Western blotting was performed using anti‐c‐Myc antibody and chemiluminescence to detect 3xMyc‐CCaMK protein (expected molecular weight = 66 kDa; upper panel); protein loading control (Ponceau S; lower panel). (b) Total protein was extracted from T0 barley plants transformed with constructs over‐expressing M. truncatula NSP2 tagged with a C‐terminal 3xMyc‐tag. NSP2‐3xMyc was detected via a WES Protein Simple system using anti‐c‐Myc antibody as indicated (expected molecular weight = 60 kDa); protein loading control using anti‐α‐tubulin antibody. (c) Real‐time quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis of T0 barley plants from (b). Data represent mean ± standard error of results from six independent transgenic plant lines. Codon‐optimized sequences of transgenes are denoted by lower case ‘s’; the synthetic Arabidopsis thaliana UBI10 intron was additionally included in sequences as indicated (see File S1 for sequence information). CCaMK and NSP2 were expressed under the control of the maize ubiquitin promoter (pZmUBI); each lane in (a) and (b) contains protein extracted from an independent transgenic line.
