Figure 1.
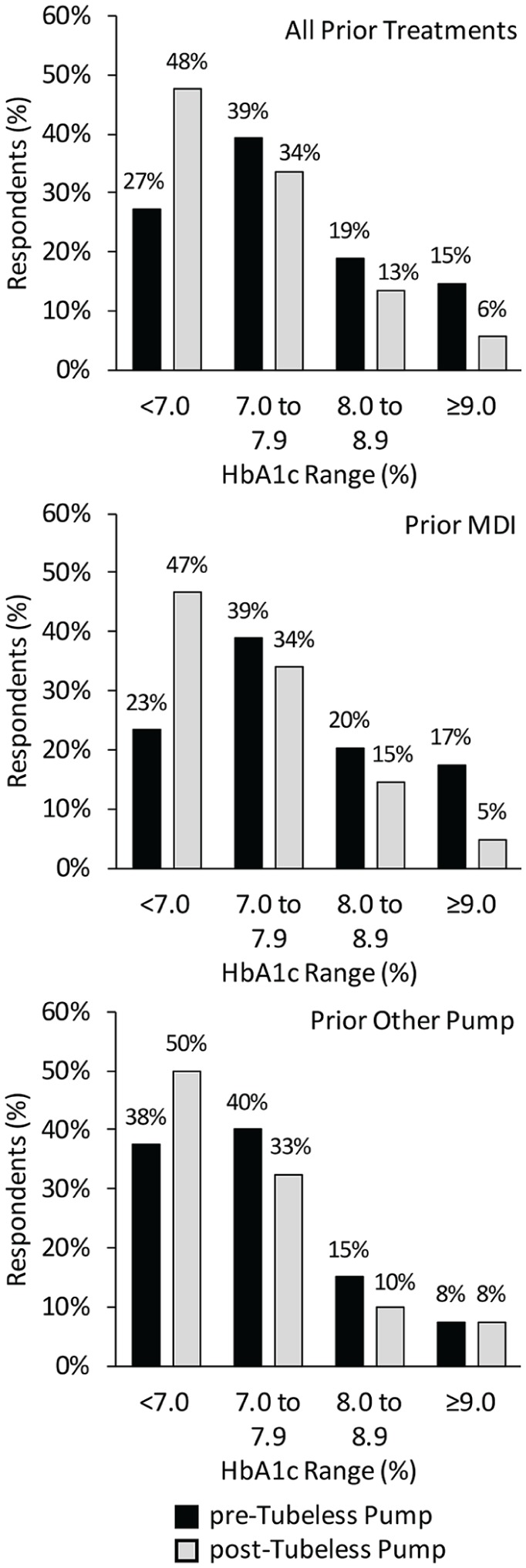
Change in self-reported HbA1c post-tubeless insulin pump therapy initiation compared to prior treatment modality.
The percentage of respondents reporting HbA1c within a given range pre-tubeless insulin pump (black bars) and post-tubeless insulin pump (gray bars) is plotted for all respondents (N = 143) and stratified by prior therapy: prior multiple daily injections (N = 103) and prior other pump (N = 40). The proportion of respondents meeting the American Diabetes Association(ADA)7 treatment target of HbA1c <7% was significantly higher post-tubeless pump overall (P < .0001) and for prior multiple daily injection users (P < .0001), and was higher for prior users of other insulin pumps but did not reach significance (P = .13). Overall, there was a significant (P < .0001) shift in self-reported HbA1c range from high to lower levels associated with tubeless insulin pump use.
