Figure EV3. MutantGFP bulge HF‐SCs are active and initiate psoriasis‐like development (related to Fig 3).
-
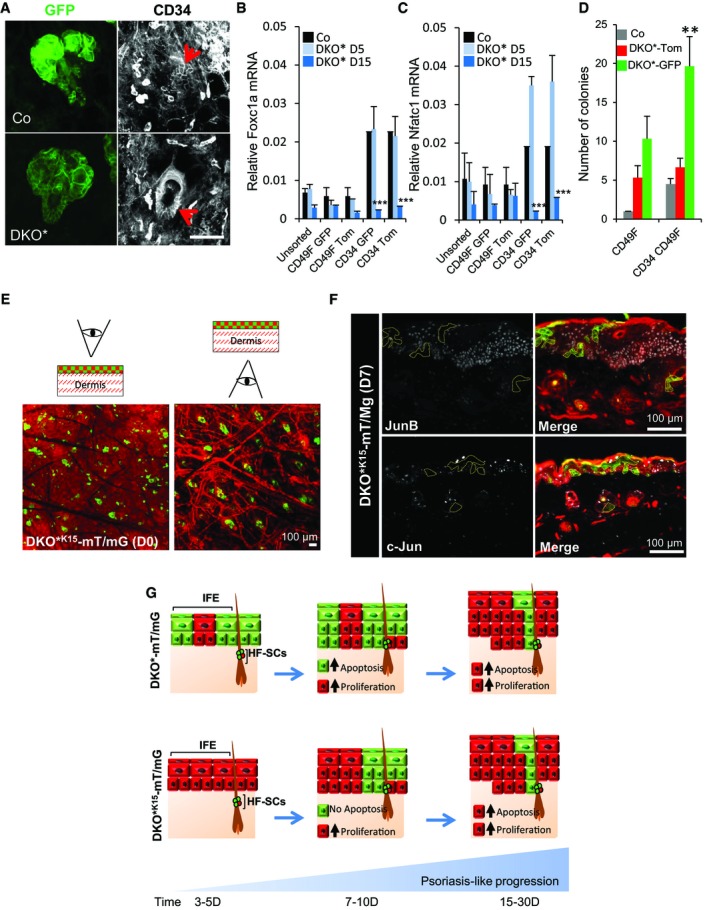
AImmunofluorescence images of the ears of control (Co) and DKO* mice showing co‐expression of mutantGFP with CD34 (red arrows) in HF‐SCs. n = 3. Scale bar = 50 μm.
-
B, CGene expression of quiescence transcription factors, Foxc1a and Nfatc1 show that HF‐SCs exit the quiescent stage during psoriasis‐like development in DKO* mice. n = 3 mice per group. Data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance ***P < 0.001 (Student's two‐tailed t‐test relative to control group). See Appendix Table S2 for exact P‐values.
-
DColony formation in vitro of bulge hair follicle stem cells (HF‐SCs, CD34+ CD49fhigh) vs. basal keratinocytes (b‐KCs, CD49fhigh) from control and DKO*‐mT/mG ears shows that mutantGFP HF‐SCs have significant increased colony formation when compared to non‐mutantTom HF‐SCs or control HF‐SCs. n = 3 mice per group. Data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance **P < 0.01 (Student's two‐tailed t‐test relative to control groups). See Appendix Table S2 for exact P‐values.
-
ERepresentative images of whole mount of ear skin from DKO*K15‐mT/mG at day 0 after mifepristone treatment in two views from the epidermis and from the dermis, to distinguish the expression of GFP+ epidermal cell in IFE and HFs.
-
FImmunofluorescence images of c‐Jun and JunB staining in DKO* K15‐mT/mG at days 5–7 after tamoxifen treatment show GFP+ keratinocytes are negative for c‐Jun and JunB expression.
-
GRepresentation of both epidermal lineage‐tracking system, DKO*‐mT/mG and DKO* K15‐mT/mG, for investigating the origin and contribution of epidermal stem cells in the development of psoriasis‐like.
