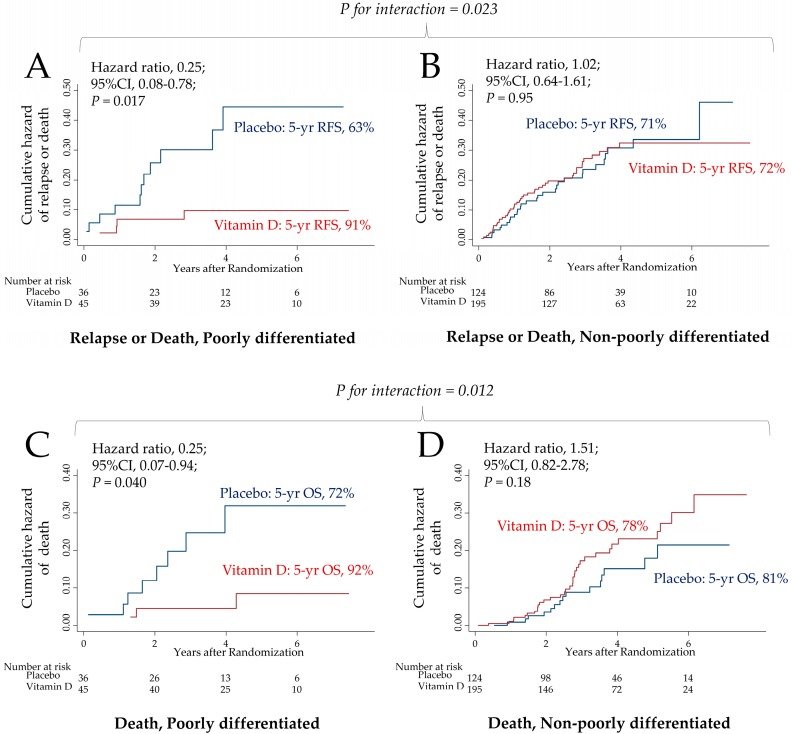
Figure 2.
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on risk of relapse or death and risk of death: Poorly differentiated vs. non-poorly differentiated. Cumulative hazard curves between vitamin D or placebo were compared (A) for relapse or death in the poorly differentiated subgroup, (B) for relapse or death in the non-poorly differentiated subgroup, (C) for death in the poorly differentiated subgroup, and (D) for death in the non-poorly differentiated subgroup. P value was determined using a Cox proportional hazards model. P for interaction between the assigned intervention (vitamin D or placebo) and the histopathological subgroups (poorly differentiated or non-poorly differentiated) was tested based on a Cox regression model. CI, confidence interval.