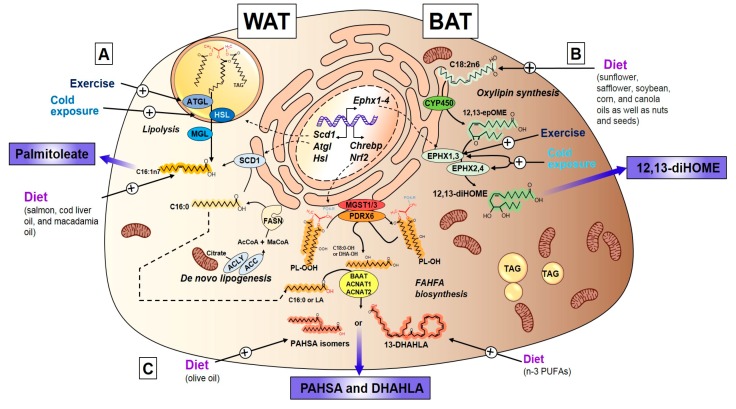
Figure 1.
Lipokine synthesis in WAT and BAT. Bioactive lipids termed lipokines are synthesized primarily in adipose tissue from white (WAT) and brown (BAT) adipose depots. (A) Palmitoleate can be synthesized in WAT from de novo lipogenesis, starting with the cleavage of mitochondrial citrate by ACLY, followed by the rate limiting enzymes ACC and FASN, generating palmitate or palmitic acid, and further desaturated by Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase (SCD1) into palmitoleate. Palmitoleate can also be obtained from sympathetic-induced, exercise-induced, and cold-induced lipolysis (HSL, ATGL, and MGL) of triglycerides (TAG), which generates the diacylglycerol (DAG) or free fatty acid (FFA) form of palmitoleate. Lastly, palmitoleate can be obtained directly from the diet and provide a bioactive form of cis-palmitoleate or trans-palmitoleate. (B) 12, 13-diHOME (12,13-dihydroxy-9Z-octadecenoate) lipokine is primarily synthesized from BAT from essential fatty acid linoleic acid provided in the diet. The first synthetic step involves CYP 450 group of enzymes that give rise to the epoxide 12, 13-epOME, and is hydrolyzed by ER-residing or cytosolic EPHX1/3 or EPHX2/4, respectively. The final hydrolysis step generates 12, 13-diHOME. Both exercise and cold exposure are strong activators of the last step (Ephx1-4) of 12, 13-diHOME synthesis. (C) Fatty acid hydroxy fatty acid (FAHFAs) constitute a novel lipid class that act as lipokines including 5-PAHSA, 9-PAHSA, and 13-DHAHLA. FAHFA synthesis is thought to start with the modulation of oxidative stress by Nrf2 and de novo lipogenic factor Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein (ChREBP), which regulate the peroxide formation and synthesis of fatty acids. The first step involves the generation of a phospholipid peroxide substrate obtained from membrane residing phospholipids spontaneously oxidized or generated by flavin-containing monooxygenases. The first committed step involves the conversion of the peroxide into a phospholipid with the hydroxy fatty acid by GSH-requiring peroxidases MGST1/3 and PDRX6. This hydroxy-fatty acyl is released from phospholipid and then coupled to an Acyl-CoA generated in de novo lipogenesis, (i.e., palmityl-CoA). This is completed by the action of acyl transferases ACNAT1, ACNAT2, and BAAT. This last step creates FAHFAs with either isomers of PAHSA or DHAHLA. ACLY: ATP-citrate lyase. FASN: Fatty Acid Synthase. ACC: Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase. SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. HSL: Hormone-sensitive lipase. ATGL: Adipose tissue triglyceride lipase. MGL: Monoglyceride lipase. CYP 450: Cytochrome P450. EPHX1-4: Epoxide Hydrolase 1-4. GSH: Glutathione. MGST1/3: Microsomal Glutathione S-Transferase 1/3. PDRX6: Peroxiredoxin 6. ACNAT1/2: Acyl-coenzyme A amino acid N-acyltransferase 1. BAAT: Bile acid-CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase.