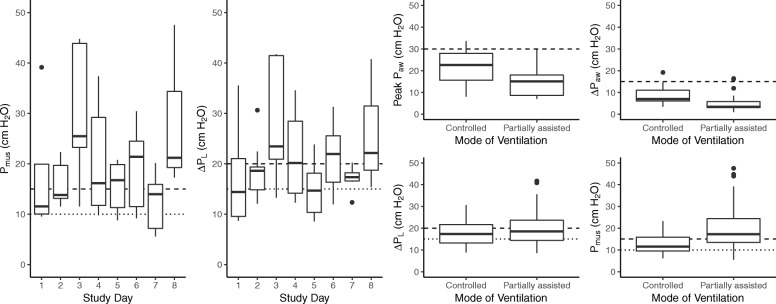
Fig. 2.
Distribution of ΔPL (dynamic transpulmonary driving pressure) and Pmus (respiratory muscle pressure) during mechanical ventilation. Pressures frequently exceeded “probably excessive” and “definitely excessive” thresholds (dotted and dashed lines, respectively) irrespective of the duration of the study or the mode of ventilation. While peak and driving airway pressures were lower under partially assisted modes of ventilation (p < 0.001 for both comparisons), transpulmonary pressure swings were not significantly different (p = 0.16)