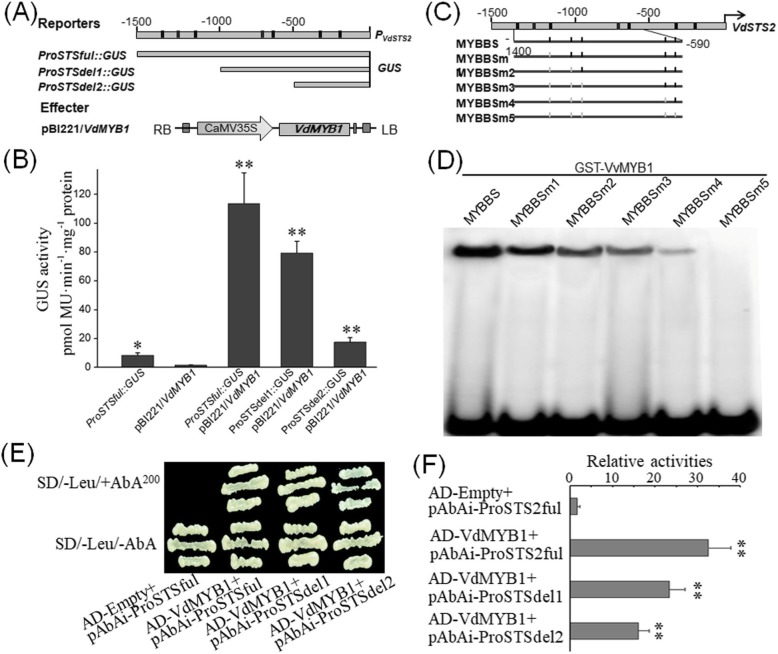
Fig. 5.
VdMYB1 binds to the promoter of VdSTS2. a Schematic representation of reporter and effector constructs. Deletion variants of the VdSTS2 promoter were cloned into the pC0390GUS vector to drive the expression of GUS reporter. The pC0390GUS empty vector was used as a negative control. The full-length cDNA of VdMYB1 was cloned into pBI221 vector to serve as an effector. b Measurement of GUS activity in Arabidopsis leaf protoplasts after the co-transformation of reporter and effector constructs. Samples were analyzed at 24 h after co-transformation. Error bars indicate SD of three independent experiments. c Schematic representation of the mutated MYB TF binding sites (MBSBSs) in the VdSTS2 gene promoter. d EMSA showing that VdMYB1 specifically binds to the VdSTS2 promoter. Purified GST-VdMYB1 protein was incubated with 32P-labeled DNA probes (STS2 promoter fragments) and subjected to EMSA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Competition for the formation of protein-DNA complex was performed using 50X unlabeled probes. e Analysis of the transcriptional activation function of VdMYB1 using yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) assay. Transformed yeast cells were examined by the growth performance on SD/−Leu supplemented with 200 mg/L of AbA. The GAL4 activation domain (AD) empty vector and pAbAi-proVdSTS2ful vector were used as negative controls. f Activity of β-galactosidase transformed yeast cells as described in (e). Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-test in different samples (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001)