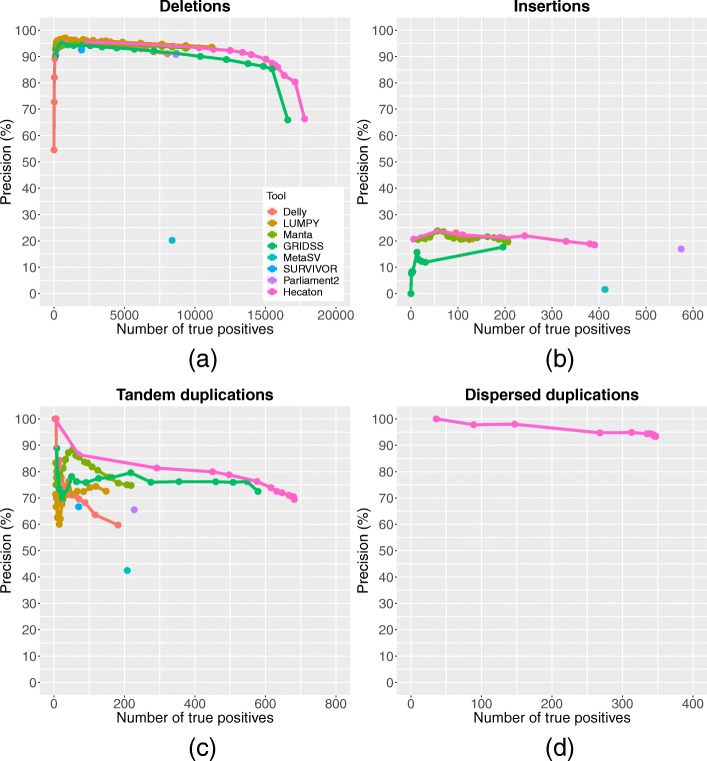
Fig. 5.
Performance of different CNV detection algorithms on short read data of the maize B73 accession. CNV calls were called relative to the maize Mo17 reference assembly. Precision-recall curves of Delly, LUMPY, Manta, and GRIDSS were constructed by varying the minimum number of discordantly aligned read pairs and/or split reads supporting each call in the set. The curve of Hecaton was produced by varying the threshold of the probabilistic score used to define calls as true positives. Performance is shown separately for deletions (a), insertions (b), tandem duplications (c), and dispersed duplications (d). Curves of LUMPY and SURVIVOR are missing for insertions, as these tools are unable to detect this type of CNV. Curves are missing for all tools besides Hecaton for dispersed duplications, as Hecaton is the only tool that can detect this type of CNV, owing to its post-processing stage. Hecaton generally improved recall and precision compared to Delly, LUMPY, Manta, and GRIDSS. Moreover, it significantly outperformed MetaSV, SURVIVOR, and Parliament2, three ensemble approaches applicable to plant data