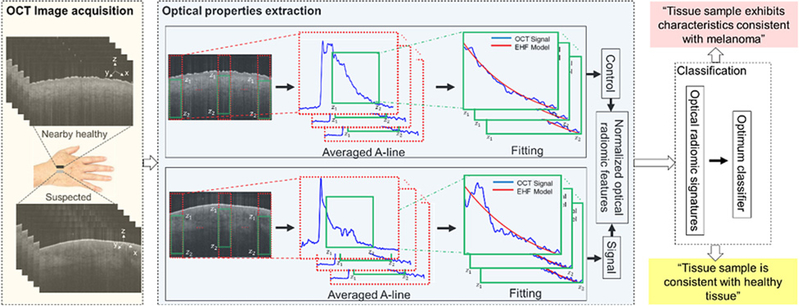
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the principles of the optical radiomic melanoma detection protocol. The steps include: acquisition of OCT images from suspected and a nearby healthy skin; the OCT B-scans are preprocessed; optical properties are extracted from the green box (z1 and z2 represent the start and end points of the ROI) by fitting the EHF model to intensity profile of the averaged A-line obtained from the ROI; the values are the mean and SD of scattering coefficient, absorption coefficient, and anisotropy factor extracted from the suspected (we call it signal) and nearby healthy (we call it control) skin to create a set of normalized optical radiomic features; the selected optical radiomic features, that is, optical radiomic signatures, with the optimum classifier evaluate the status of the tissue: “Tissue sample is consistent with healthy tissue,” “Tissue sample exhibits characteristics consistent with melanoma.”