Figure 3. RIP1i-mediated tumor-protection is CD4+ and CD8+ T cell dependent and is synergistic with PD-1 blockade and ICOS agonism.
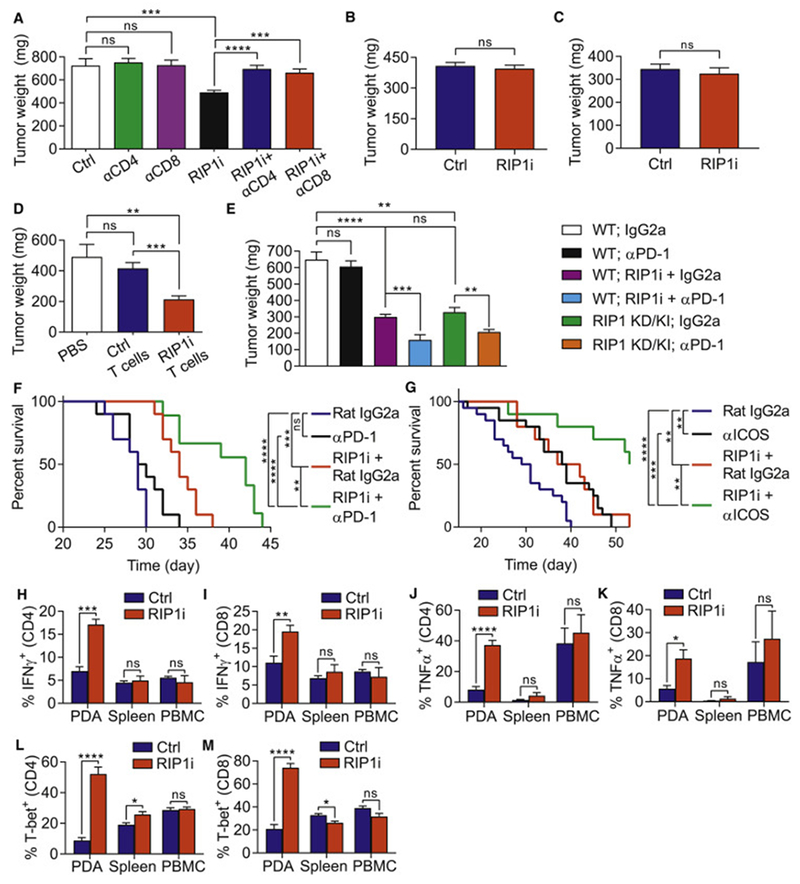
(A) Tumor weight of WT mice bearing KPC-derived tumor treated with neutralizing mAbs against CD4 or CD8 or with isotype control alone or in combination with RIP1i or control and sacrificed at 21 days (n=10/group). This experiment was repeated twice. (B, C) Tumor weights of WT and Foxn1nu mice (B, n=7/group) and of WT and Rag1−/− mice (C, n=5/group) challenged with orthotopic KPC tumor cells and sacrificed at 3 weeks. Each experiment was repeated twice. (D) Tumor weights of WT mice orthotopically implanted with KPC-derived tumor cells alone or admixed with tumor-infiltrating T cells harvested from control PDA or from PDA in RIP1i-treated mice (n=8/group) and were sacrificed on day 21. This experiment was repeated twice. (E) Tumor weight of WT or RIP1 KD/KI mice (n=8/group) orthotopically implanted with KPC-derived tumor cells and treated as indicated. Mice were sacrificed at 21 days. This experiment was repeated 3 times. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice administered with a portal venous injection of KPC-derived tumor cells and treated as indicated beginning on day 5 after tumor challenge (n=10/group). This data represents one of two repeat experiments. (G) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice orthotopically implanted with KPC-derived tumor cells and treated as indicated (n=10-20/group). This data represents one of two repeat experiments. (H-M) Expression of IFNγ (H, I), TNFα (J, K), and T-bet (L, M) in PBMC, spleen, and PDA-infiltrating CD4+ (H, J, and L) and CD8+ (I, K, and M) T cells from WT mice orthotopically implanted with KPC-derived tumor cells and treated with RIP1i or control and sacrificed at 21 days. These experiments were repeated twice. Data are displayed as average ± SEM (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001). See also Figure S3.
