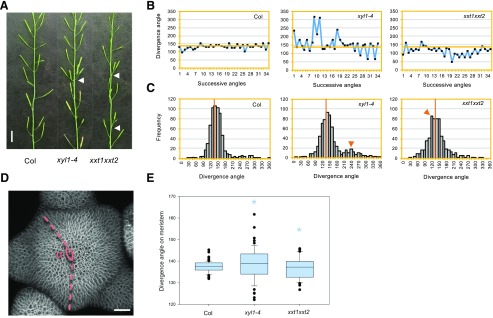
Figure 4.
Phyllotactic phenotype of XyG mutants. A, Representative image showing perturbation of phyllotaxis (indicated by arrowhead) in xyl1-4 and xxt1xxt2 mutants. Scale bar = 1 cm. B, Representative distribution angles of siliques on the inflorescence stem of Col, xyl1-4, and xxt1xxt2 plants. C, Distribution of divergence angles of siliques on the Col, xyl1-4, and xxt1xxt2 inflorescence stems. Orange lines denote the position of a divergence angle of 137°. Orange arrowheads mark the abnormal angle peaks; n = 649 angles from 20 Col plants; n = 683 angles from 21 xyl1-4 plants; n = 635 angles from 21 xxt1xxt2 plants. D, Diagram showing the method to measure the divergence angles (⍺) between successive primordia on confocal images of live meristems. Scale bar = 20 µm. E, Primordia distribution angles on Col, xyl1-4, and xxt1xxt2 meristems; n = 67 angles from 11 Col meristems; n = 55 angles from 6 xyl1-4 meristems; n = 46 angles from 8 xxt1xxt2 meristems. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences with wild type; *P < 0.05, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.