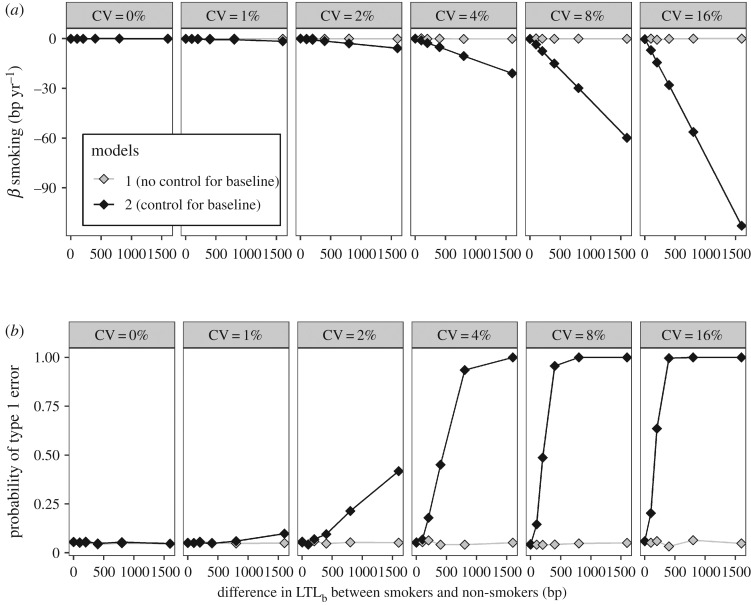
Figure 4.
The bias caused by controlling for LTLb is a synergistic interaction between difference in LTLb and measurement error. The data in this figure come from a simulation of scenario C only (a true difference in LTLb, but no difference in ΔLTL). (a) The estimated difference in mΔLTL between smokers and non-smokers as a function of the difference in LTLb and CV for models 1 and 2. Data points are the mean ± 95% confidence intervals obtained from modelling the data from 1000 replicate simulations. (b) The probability of a type 1 error as a function of the difference in LTLb and CV for models 1 and 2. Data points represent the proportion of simulations yielding a p-value below 0.05 in 1000 replicate simulations.